Achilles Tendon Problems
Overview: Understanding Achilles Tendon Problems
The Achilles tendon is a strong, fibrous cord present at the back of your lower leg connecting your calf muscles to your heel bone. Its primary function is to assist in walking by raising the heel off the ground. However, this tendon can rupture or become inflamed, leading to a range of Achilles tendon problems, which can significantly affect mobility. Estimates suggest that Achilles tendonitis alone affects approximately 11% of running athletes.
Types: Recognizing Different Achilles Tendon Problems
Achilles tendon problems primarily fall into two categories:
-
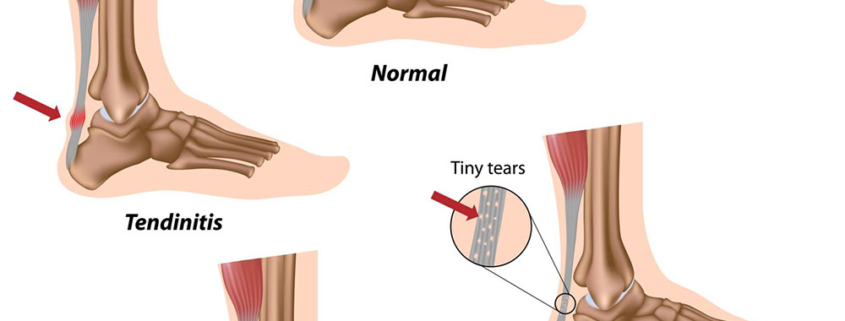
- Achilles Tendonitis: Inflammation of the Achilles tendon primarily caused by overuse, leading to pain and swelling.
-
- Achilles Tendon Rupture: A more severe injury usually associated with a sudden, sharp pain in the heel area. This happens when the tendon is partially or completely torn.
Causes: Common Risk Factors
The Achilles tendon is vulnerable to injury primarily due to strain and overuse. Other risk factors include:
-
- Age: As we grow older, the tendon weakens, increasing susceptibility to injury.
-
- Sex: Achilles tendon problems are more common in men than women.
-
- Physical Factors: Flat feet, a tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles, or overweight/obesity can put more strain on the Achilles tendon.
-
- Intense Physical Activity: Sudden increases in exercise intensity or duration can injure the tendon.
-
- Incorrect Footwear: Shoes that do not support the arch properly or are worn out can lead to Achilles tendon injuries.
Symptoms: Identifying Achilles Tendon Problems
The most common symptoms of Achilles tendon problems include:
-
- Pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon in the morning
-
- Pain along the tendon or back of the heel that worsens with activity
-
- Severe pain the day after exercising
-
- Sudden and acute pain, indicating possible rupture
-
- Swelling that worsens with activity
-
- Inability to stand on the toes
Diagnosis: How Achilles Tendon Problems are Identified
Achilles tendon problems are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. Your doctor may examine your foot and ankle to check for pain, swelling, or a gap in the tendon if a rupture is suspected. Imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs can also be helpful to visualize the tendon.
Treatment Options: Managing Achilles Tendon Problems
Treatment of Achilles tendon problems depends on the severity of the injury, and could include:
-
- Rest: Avoid activities that provoke pain.
-
- Ice: Apply cold packs for 20 minutes at a time throughout the day to reduce swelling.
-
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises can help restore mobility and strength.
-
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation.
-
- Orthotic Devices: Shoe inserts or braces can help support the tendon and reduce pain.
-
- Surgery: Severe cases like a ruptured Achilles tendon might necessitate surgical intervention.
Living With Achilles Tendon Problems: Practical Tips
Living with an Achilles tendon problem can initially be challenging. Some helpful tips include:
-
- Start slow with gentle movement and gradually build up activity levels to avoid overstraining the tendon.
-
- Maintain flexibility with regular stretching exercises.
-
- Stay at a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the tendon.
-
- Wear appropriate, supporting footwear and use orthotics if required.
-
- Listen to your body and rest if in pain.
When to Seek Help: Get Medical advice
It’s vital to seek immediate medical attention if you:
-
- Feel a sudden ”pop” in the back of your calf or heel
-
- Have severe pain in your Achilles tendon
-
- Cannot walk or bear weight on your foot
-
- Have significant swelling in your heel or calf
Remember, early intervention can significantly enhance recovery and reduce the risk of further complications.
