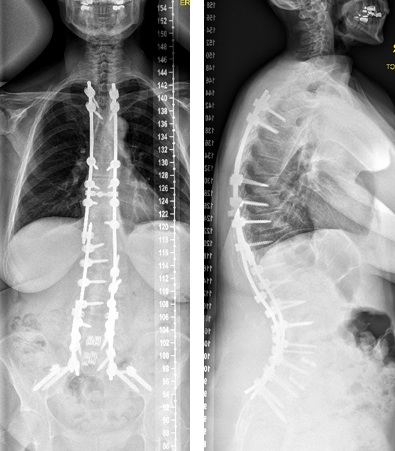
Adult Degenerative Scoliosis
Overview
Adult degenerative scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine that develops over time. It most often occurs in adults over the age of 50. Unlike scoliosis in children, which often is caused by congenital factors or neuromuscular issues, adult degenerative scoliosis usually develops as the spine ages and the vertebrae degenerate. It is estimated that about 60% of older adults may have some form of scoliosis, but not all cases require treatment.
Types
There are mainly two types of scoliosis in adults:
-
- Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: This type begins in childhood or adolescence and can continue into adulthood. While many adolescents do not require treatment, some may experience problems later in life.
-
- Degenerative Scoliosis: This type develops in adults due to wear and tear on the spine from aging, osteoporosis, or degenerative disc disease.
Causes
The exact cause of adult degenerative scoliosis can vary, but the following factors contribute to its development:
-
- Age: The natural aging process can lead to degeneration of the spinal discs and joints.
-
- Genetics: A family history of scoliosis can increase the risk.
-
- Osteoporosis: Weakened bones can lead to structural changes in the spine.
-
- Previous spinal surgery or injury: History of trauma or prior operations on the spine can lead to degenerative changes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of adult degenerative scoliosis can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
-
- Pain: Chronic back pain is the most frequent complaint.
-
- Muscle spasms: Tightness or spasms in the back muscles can occur.
-
- Numbness or tingling: Nerve compression may cause these sensations in the legs.
Less common symptoms can include:
-
- Difficulty standing up straight: Patients may notice they lean to one side.
-
- Fatigue: Prolonged standing or walking may lead to body fatigue.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of adult degenerative scoliosis generally involves several steps:
-
- Medical History: A thorough discussion about symptoms and health history.
-
- Physical Examination: A doctor examines the spine for curvature and assesses any discomfort or limitations.
-
- X-rays: Images of the spine provide a clear view of its curvature and structure.
-
- MRI or CT Scan: These imaging tests can show more detailed pictures of the spine, including nerves and surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options
Treatment for adult degenerative scoliosis varies based on symptoms and severity. Options include:
Conservative Treatments
-
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can relieve pain.
-
- Physical Therapy: Customized exercises can strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
-
- Bracing: In some cases, a spinal brace may help relieve pressure on the spine.
Surgical Treatments
When conservative methods are ineffective, surgery may be considered. Surgical options can include:
-
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves joining two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
-
- Decompression Surgery: If nerves are compressed, this surgery can help alleviate the pressure.
Living With Adult Degenerative Scoliosis
Managing adult degenerative scoliosis involves several lifestyle changes and coping strategies:
-
- Stay Active: Engage in regular, low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
-
- Practice Good Posture: Maintain proper posture while sitting and standing to reduce strain on the spine.
-
- Use Heat or Ice: Applying heat or ice can help alleviate pain and muscle spasms.
-
- Consider Therapy: Psychological or physical therapy can help address pain management and emotional coping strategies.
When to Seek Help
It’s important to recognize when to seek further medical assistance. Contact your doctor if you experience:
-
- Sudden or severe back pain that is not relieved by rest or over-the-counter medications.
-
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs.
-
- Difficulty walking or standing straight.
-
- Unexplained weight loss or changes in bowel or bladder function.
If you have concerns about your spine or how to manage your symptoms effectively, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and support.