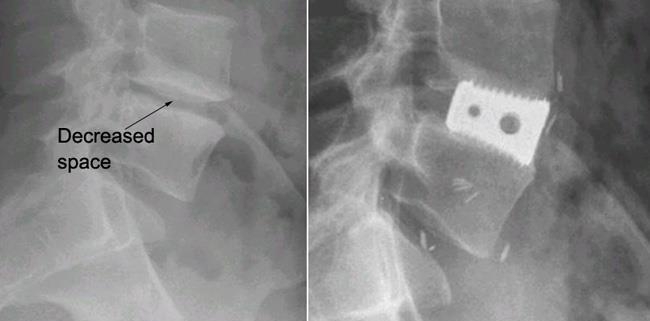
Anterior Lumbar Fusion with Cages
Overview
Anterior Lumbar Fusion with Cages, commonly abbreviated as ALIF, is a neurosurgical technique that strives to mitigate back pain and correct spinal deformities. During an ALIF procedure, the surgeon accesses the lumbar spine from the front, thus safeguarding valuable back muscles from potential pathological interference. The procedure prevalently treats conditions like degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, and disc herniation.
Types
While Anterior Lumbar Fusion is a specific type of surgical treatment for back pain, it can be classified based on different levels of the fusion and the type of cages used.
– Single-level ALIF: This entails fusing one segment of the spine, where the problematic disc is located.
– Multi-level ALIF: Here, more than one segment of the spine is fused.
The types of cages used can be categorized into:
– Metal cages: Typically comprised of titanium.
– Plastic cages: Usually made from PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone).
Causes
ALIF is used to treat various conditions, predominantly caused by the aging process, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle factors like poor posture, lack of physical activity, or obesity. These conditions include:
- Disc herniation
– Degenerative disc disease
– Spondylolisthesis
– Spinal stenosis
– Chronic lower back pain
Symptoms
Patients requiring an Anterior Lumbar Fusion with Cages surgery typically exhibit symptoms such as:
– Chronic lower back pain that doesn’t improve with conservative treatment.
– Unexplained weakness or numbness in the legs or feet.
- Difficulty standing or walking for long periods due to discomfort.
– Pain that radiates down one or both legs.
Please note that these symptoms could signify other medical issues and it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if such symptoms persist.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing the need for an ALIF procedure involves a comprehensive examination. This typically includes patient history, physical examination, radiographic imaging (such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs), and occasionally nerve conduction studies.
Treatment Options
Treatment options span from conservative management to surgical intervention:
– Conservative management: This includes lifestyle changes, physical therapy, pain management using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, muscle relaxants or steroid injections.
– Surgical management: If conservative treatments don’t yield sufficient results, surgery such as decompression laminectomy or spinal fusion surgery like ALIF may be considered.
Living With Anterior Lumbar Fusion with Cages
Post-surgery, patients are encouraged to follow specific tips to ensure a successful recovery:
– Adhere strictly to prescribed medication.
– Engage in mild physical activities such as walking as recommended by the doctor.
– Gradually resume normal activities under the guidance of a physical therapist.
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical attention if:
– Pain escalates or spreads to new areas.
– Experiencing increased weakness or numbness in the legs.
– Notice signs of infection at the incision site, such as redness, swelling, or discharge.
This guide provides a general outline; however, each patient’s case is unique. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs and concerns with your healthcare provider.
