Artificial Joint Replacement of the Thumb
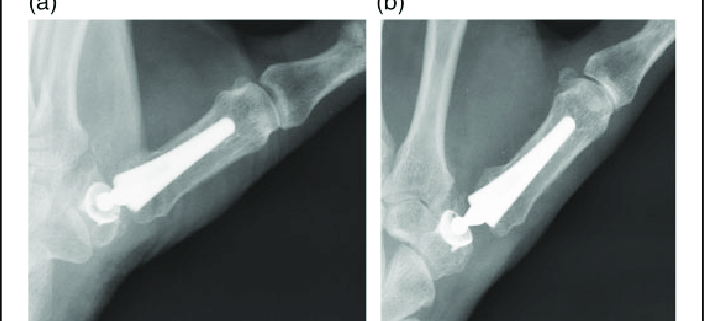
Overview
Artificial joint replacement of the thumb, often referred to as thumb arthroplasty, involves replacing a damaged or diseased thumb joint with an artificial one. This surgical procedure aims to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and improve the quality of life for patients experiencing thumb joint issues. Millions of people worldwide undergo this procedure every year seeking relief from severe pain and the return of function in their thumb.
Types
There are two main types of thumb joint replacement, based on the specific joint in the thumb that is replaced.
1. Carpometacarpal (CMC) Joint Arthroplasty: This procedure involves replacing the joint at the base of the thumb, where it connects to the wrist. It is commonly performed for individuals with arthritis in this joint.
2. Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) Joint Arthroplasty: This procedure involves replacing the joint in the middle of the thumb. It’s commonly performed for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis affecting this joint.
Causes
The need for thumb joint replacement often arises due to chronic degenerative diseases such as Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, or injury. These conditions can cause the joint to wear away, leading to pain and impaired function in the thumb.
Symptoms
Individuals who may need an artificial joint replacement of the thumb typically experience:
-
- Persistent thumb pain
-
- Decreased strength in the thumb
-
- Difficulty with gripping or pinching
-
- Thumb joint stiffness or swelling
-
- Visible deformity or changes in thumb appearance
Diagnosis
The diagnosis generally involves a physical examination, discussion of symptoms, and medical history review. Imaging tests such as X-rays or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can aid in assessing the extent of joint damage and help determine the most suitable treatment option.
Treatment Options
Treatment for thumb joint issues typically begins conservatively, with rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy. If these measures are unsuccessful, surgical intervention, like joint replacement, may be considered.
Living With Artificial Joint Replacement of the Thumb
After thumb joint replacement surgery, it’s crucial to follow the recommended rehabilitation program, which may include physical therapy exercises to strengthen the thumb and improve range of motion. Medications may be prescribed to manage pain and prevent infection. Lifestyle changes such as avoiding heavy lifting and adhering to a healthy diet can support recovery and enhance overall health.
When to Seek Help
If you’re experiencing persistent thumb pain, weakness, stiffness, or difficulty performing everyday tasks with your hand, it’s essential to seek medical attention. If you have already undergone thumb joint replacement and notice signs of infection like increased pain or swelling, redness, or fever, seek immediate medical attention.
It’s crucial to remember that while artificial joint replacement of the thumb can significantly enhance quality of life, recovery requires time, patience, and diligent follow-up with healthcare providers.
