Back Muscle Strain
Overview
A back muscle strain is a common condition that occurs when the muscles in the back are stretched or torn, leading to pain and inflammation. This condition often results from physical exertion or improper lifting techniques. It is estimated that approximately 80% of adults experience lower back pain at some point in their lives, with muscle strains being a prevalent cause.
Types
While any back muscle can be strained, there are two main types of back muscle strains based on the area affected:
– Lower Back Strain: This is more common and involves strain to the muscles and ligaments in the lower back.
– Upper Back Strain: It’s less common due to the extra support provided by the rib cage in the upper back, but strains still happen from overuse or trauma.
Causes
Back muscle strain can occur due to various reasons including:
– Lifting heavy objects incorrectly
– Overuse of the muscles, such as from strenuous exercise or repetitive work tasks
– Poor posture while sitting or standing
– Direct trauma to the back
– Lack of conditioning or stretching before physical activities
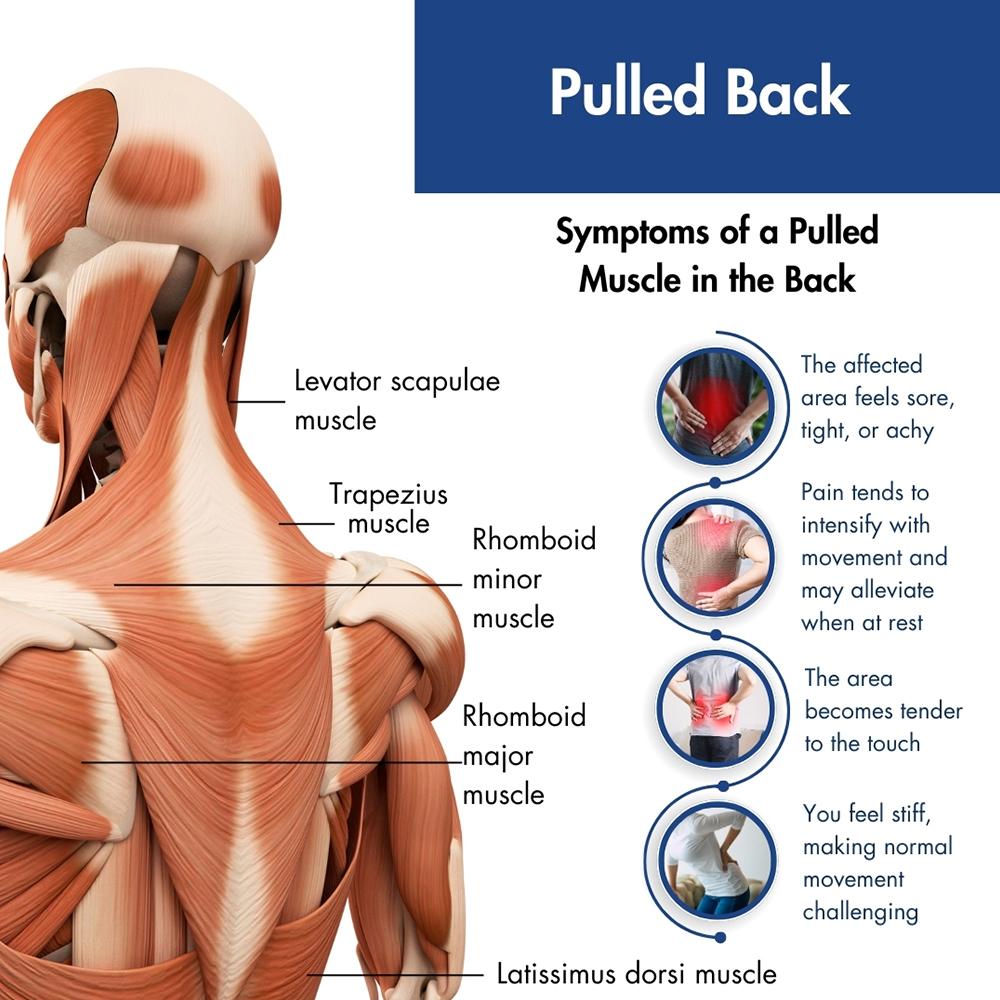
Symptoms
People with a back muscle strain may experience:
– Pain that worsens with movement
– Limited range of motion
– Muscle spasms
– Swelling or bruising in the back area
- Difficulty standing upright or walking
In rare cases, a strain can lead to chronic back pain, which may cause additional symptoms such as numbness or tingling in the lower extremities.
Diagnosis
To diagnose a back muscle strain, a healthcare provider typically:
– Asks about your symptoms and medical history
– Performed physical examination
– May order imaging tests such as an X-ray, MRI or CT scan to rule out other conditions
It’s important to note that while a muscle strain could be an underlying cause, these tests cannot directly identify a strain.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a back muscle strain focuses on relieving pain and promoting healing. Options include:
– Rest: Limiting activity can help reduce inflammation and prevent further injury.
– Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen your back and promote flexibility can be beneficial.
– Over-the-Counter Medications: Non-prescription pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help with pain and swelling.
– Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying ice to the area can reduce inflammation, while heat can help relax the muscles.
In severe cases, where the pain and disability are significant, a healthcare provider might suggest surgery as a last resort.
Living With Back Muscle Strain
Living with back muscle strain requires patience, relaxation, and care. Tips include:
– Rest and avoid reinjuring your back
– Practice regular gentle exercise after the initial pain subsides to rebuild strength and flexibility
- Use good posture when sitting and standing
– Practice safe lifting techniques
– Maintain a healthy weight to minimize pressure on your back
When to Seek Help
While muscle strains generally improve with self-care, you should seek medical attention if:
– Pain persists despite self-care measures
– Pain is severe or worsening
– There are symptoms like weakness, numbness or tingling down the legs
– You experience difficulty with walking, standing, or bladder/bowel control
These could signal a more serious condition that may require urgent treatment. Always listen to your body and consider professional advice when in doubt. And remember, while anyone can experience back muscle strain, lowering risk factors and practicing good back care can help you protect your musculoskeletal health.
