Cervical Burners and Stingers (Brachial Plexus Injuries)
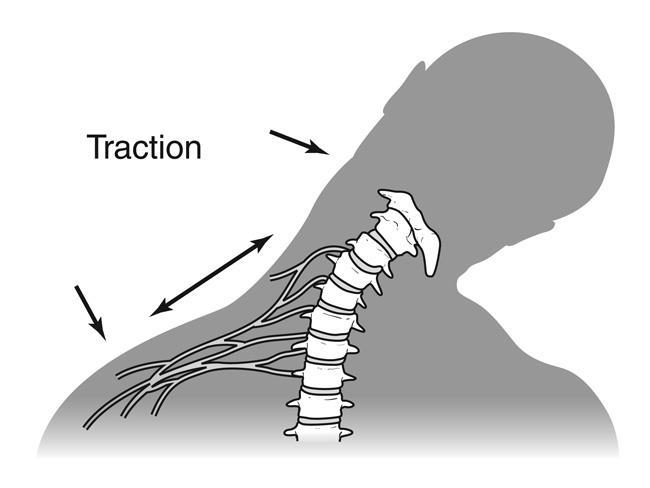
Overview
Cervical burners and stingers, also known as brachial plexus injuries, are common terms in the sports medicine field. These are injuries that result from damage to the nerves in the neck and shoulder area known as the brachial plexus. The injury often creates a burning or stinging sensation, hence the name. This is a common injury among athletes, especially those involved in high-impact sports like football or rugby. However, these conditions are not limited to sports; they can also occur due to everyday activities and accidents involving trauma to the neck and shoulder.
Types
Brachial plexus injuries are typically classified into two types based on severity: Neuropraxia and Axonotmesis.
-
- Neuropraxia: This is the most common type and it happens when the nerve gets stretched or compressed but doesn’t tear. Symptoms usually disappear within a few seconds or minutes.
-
- Axonotmesis: It is a more severe type as the nerve gets damaged or torn. The recovery is slower and may require medical intervention.
Causes
The main cause of cervical burners and stingers is direct or indirect trauma to the neck or shoulder, causing damage to the brachial plexus. This can happen during contact sports such as football or wrestling, or from other accidents such as falls or car accidents. In some cases, they can also be caused by diseases or conditions that cause nerve inflammation like arthritis.
Symptoms
Some common symptoms of cervical burners and stingers include:
-
- A sudden severe burning or stinging pain in the neck, shoulder or arm.
-
- Weakness or numbness in the arm or hand.
-
- Decreased ability to move the affected arm.
It is important to note that symptoms usually affect only one side of the body and can disappear quickly (within minutes) or last for several days.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing cervical burners and stingers involves a physical exam and an analysis of the patient’s medical history. The doctor may perform tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to assess any damage or inflammation. In some instances, they may carry out nerve conduction tests to determine the extent of nerve injury.
Treatment Options
The treatment of cervical burners and stingers primarily aims to relieve pain and restore normal function of the affected area. Treatment options can include:
-
- Conservative Approach: Rest and ice application can help reduce swelling and discomfort. Over-the-counter pain medication can also be used to manage pain.
-
- Physical Therapy: It may be recommended to strengthen muscles and increase flexibility. This approach aims to help to restore the full range of motion and prevent future injuries.
-
- Surgery: In severe cases where the nerve is torn, surgery may be required to repair the damaged nerve.
Living With Cervical Burners and Stingers (Brachial Plexus Injuries)
As with living with any condition, it’s important to take steps to manage your cervical burners or stingers. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider and adherence to prescribed therapy are key. A balanced diet, mild forms of exercise like stretching or yoga, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help reduce pain and prevent future injuries.
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe or persistent neck, shoulder, or arm pain, prolonged weakness or numbness, or if symptoms do not improve within a few days. Remember, an unwarranted delay in seeking help can lead to worsening of the condition and potential long-term damage. A consultation with a medical professional can provide a correct diagnosis and timely treatment.
