Cervical Laminectomy
Overview
Cervical laminectomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or spinal nerves. It is most commonly done to treat spinal stenosis, which is a narrowing of the spinal canal. This procedure involves removing the bone (laminae) at the rear of the vertebrae in the neck (cervical spine) to create more space for the nerves. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, nearly 500,000 people in the U.S.A undergo a laminectomy or a related procedure each year.
Causes
The main cause necessitating a cervical laminectomy is spinal stenosis. It is a condition primarily caused by wear and tear changes in the spine related to aging. In severe cases of spinal stenosis, doctors might recommend a cervical laminectomy.
Risk factors for spinal stenosis include:
-
- Age: The condition is most common in people over 50.
-
- Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
-
- Genetics: Some people are born with a small spinal canal.
-
- Spinal injuries.
-
- Previous surgery of the spine.
Symptoms
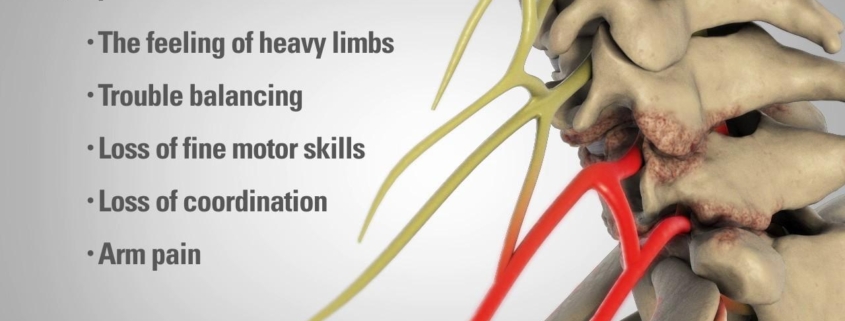
Symptoms of spinal stenosis can include:
-
- Pain in the neck or back
-
- Numbness, weakness or tingling in the hands, arms, feet or legs
-
- Balance problems
-
- Bladder or bowel issues in severe cases
Diagnosis
Spinal stenosis and the need for a cervical laminectomy can be diagnosed with a physical exam and medical history review. In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests like X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans to get a better view of your spine.
Treatment Options
Treatment for spinal stenosis ranges from lifestyle changes and medication to surgery in severe cases.
Before recommending surgical interventions such as a cervical laminectomy, physicians often explore non-surgical treatments including:
-
- Physical therapy
-
- Pain medication (over-the-counter or prescription)
-
- Epidural steroid injections
If those treatments don’t provide enough relief, surgery may be an option. Surgical treatments include:
-
- Cervical laminectomy: Removal of the laminae to create more space for the nerves.
-
- Laminoplasty: Another operation to make more space for the spinal cord and nerve roots.
-
- Fusion surgery: Joining two vertebrae together to limit motion and prevent instability.
Living With Cervical Laminectomy
After surgery, rehabilitation is necessary to regain strength and mobility. This includes physical therapy and home exercises.
It can sometimes take several weeks to return to normal activities after a cervical laminectomy, and you may need to make changes like avoiding certain activities or modifying your workspace.
Managing pain post-surgery typically includes medication. It’s also important to closely follow the surgeon’s instructions about wound care and follow-up appointments to ensure successful healing.
When to Seek Help
If you’re experiencing symptoms like persistent neck or back pain, numbness, weakness, or balance problems that interfere with daily activities, it’s time to seek medical help.
For post-operative patients, seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, signs of infection at the incision site (such as redness, swelling, or discharge), loss of bladder or bowel control, or worsening neurological symptoms.
Remember that each individual’s health situation is unique. If you believe you might benefit from a cervical laminectomy, talk to your doctor about your symptoms and treatment options.
a cervical laminectomy is a crucial surgical procedure that aids in alleviating pain associated with spinal stenosis. Getting an early diagnosis and following suitable treatment options, such as surgery, can ease symptoms and improve the quality of life for people living with this condition. Be sure to discuss all your concerns and questions with your doctor to ensure you make the most informed decision about your treatment.
