Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
Overview
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), formerly known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy, is a chronic condition characterized by severe, persistent pain typically affecting one limb. The condition can develop after a trauma, surgery, stroke or heart attack. Unlike typical injuries, the pain experienced with CRPS is often much more severe than would be expected for the nature of the injury.
Types
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome is classified into two types:
-
- CRPS-I: Formerly known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD), this type can follow an illness or injury that didn’t directly damage the nerves in the affected limb.
- CRPS-II: Previously known as Causalgia, this type follows a distinct nerve injury.
Causes
While the precise cause of CRPS is not completely understood, it is believed that CRPS develops as a result of a dysfunction in the central or peripheral nervous systems. This can be triggered by injuries or surgeries, heart attacks, infections, or even sprained ankles. Factors that may increase the risk of CRPS include:
-
- Personal or family history of CRPS or other pain disorders
-
- Increased stress levels
-
- Being female - CRPS is more common in women than men
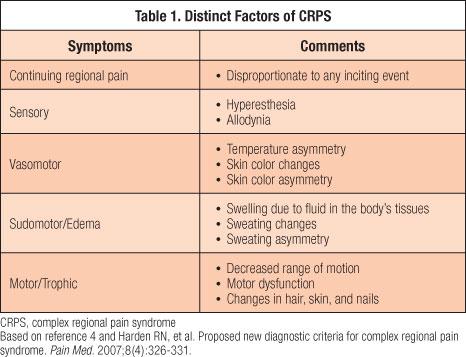
Symptoms
Key symptoms of CRPS can include:
-
- Continuous, intense pain often described as ‘burning’
-
- Swelling and stiffness in affected joints
-
- Changes in skin color, temperature, and texture
-
- Abnormal sweating and hair growth
-
- Muscle atrophy or weakness
Diagnosis
CRPS is typically diagnosed based on a physical exam and your medical history. There’s no single test that can definitively diagnose CRPS, but imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans, and bone scans may be used to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for CRPS aims to relieve painful symptoms so that people can resume their normal life and activities. Options include:
-
- Physical Therapy: To improve blood flow and flexibility.
-
- Medication: Including over-the-counter pain relievers, antidepressants, corticosteroids, and bone-loss medication.
-
- Nerve Block: This procedure can help block nerve impulses to the affected area, reducing pain.
-
- Surgical and other procedures: These may be considered for severe cases.
Living With Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
While living with CRPS can be challenging, it’s important to stay proactive about managing your condition. Some tips include:
-
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep.
-
- Pain Management: Explore different techniques like heat/cold therapy, relaxation techniques, or over-the-counter pain medicines.
-
- Seek Support: Join a support group, lean on the help of family and friends, or seek professional counseling to help cope with the emotional aspects of the condition.
When to Seek Help
If you experience intense pain, muscle atrophy, or skin changes following an injury or surgery, seek medical attention immediately. Similarly, if existing symptoms worsen or if you have ineffective pain relief, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. You don’t need to face CRPS alone; prompt treatment often provides the best results.
