Elbow Bursitis
Overview
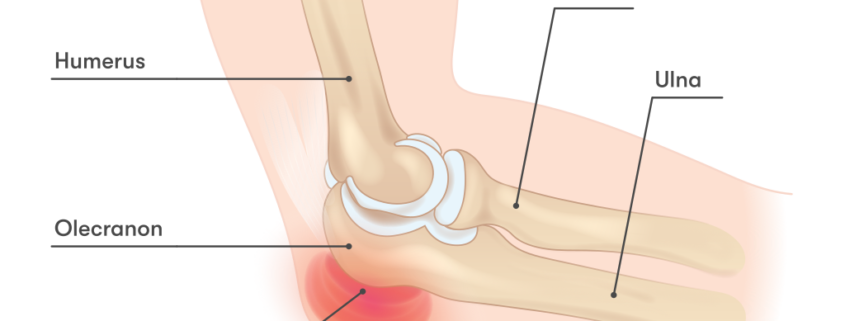
Elbow bursitis, also known as olecranon bursitis, is a condition characterized by the swelling of the bursa located at the tip of the elbow, causing pain and limited movement. The bursa is a small fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between the bones and soft tissues, reducing friction. Inflammation of this bursa leads to elbow bursitis. Though it can affect anyone at any age, it’s commonly found among those involved in repetitive motion activities that involve the elbow.
Types
Elbow bursitis can generally be categorized into two types:
-
- Septic Bursitis: This type of elbow bursitis results from a bacterial infection, hence it is also called infectious bursitis. It requires immediate medical attention.
-
- Aseptic Bursitis: It is the most common type caused by trauma, pressure, or systemic diseases like arthritis or gout.
Causes
Elbow bursitis is primarily caused by repetitive pressure or trauma to the bursa due to activities that involve leaning on the elbow for longer periods. Other factors include infection, medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or an adverse response to certain medications.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of elbow bursitis include:
-
- Swelling at the tip of the elbow
-
- Pain especially when the elbow is bent or touched
-
- Redness and warmth around the affected area
-
- Difficulty in moving the elbow
In case of septic bursitis, additional symptoms may include fever and chills.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of elbow bursitis typically involves a physical examination by healthcare professionals. They may examine the area for tenderness, warmth, and redness. They may also ask about your medical history and any recent physical activities. In some cases, a sample of the bursa fluid may be taken for further testing to rule out infection.
Treatment Options
Treatment for elbow bursitis aims to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrence. Approaches can include:
-
- Rest and Ice application: Limiting activity and applying a cold pack can help minimize swelling and pain.
-
- Medications: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation. In severe cases, a physician may inject corticosteroids directly into the bursa.
-
- Physical Therapy: Certain exercises may be recommended to improve range of motion.
-
- Surgery: In rare cases, when conservative measures are not effective, surgery may be considered to remove the infected bursa.
Living With Elbow Bursitis
Living with elbow bursitis involves managing symptoms and preventing future flare-ups. This may include wearing elbow pads to protect the elbow, performing gentle exercises to maintain flexibility, and taking medications as prescribed by your doctor.
When to Seek Help
If the swelling in your elbow is accompanied by severe pain, fever, redness, or warmth, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms could indicate an infected bursa, which requires urgent care. Additionally, if your symptoms don’t improve with initial treatments like rest and over-the-counter meds, or if they worsen, you should contact your healthcare provider.
