Foot Fractures
Overview
Foot fractures are common medical conditions that occur when one or more bones in the foot break due to an injury, overuse, or disease condition. It has been estimated that approximately 10% of all fractures occur in the 26 bones of the foot. A foot fracture can result in severe pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty in walking and performing daily activities.
Types
Foot fractures are generally classified into the following types:
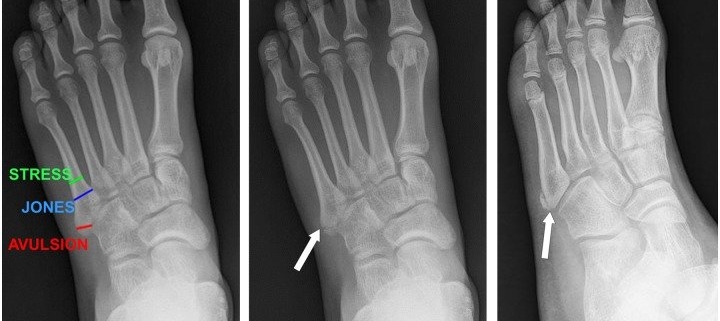
– Stress fractures: These tiny cracks are caused by overuse or repetitive activity, especially in athletes.
– Traumatic fractures: These fractures are typically due to injuries or accidents, resulting in a broken or shattered bone.
– Avulsion fractures: This type occurs when a small piece of bone is pulled off due to severe ligament pulling.
– Jones fractures: These fractures occur in a small area of the foot that receives less blood, making them more challenging to heal.
Causes
Foot fractures can occur due to a variety of reasons such as:
– Accidental falls
- Direct blow to the foot
– Repetitive activities or overuse
– Diseases like osteoporosis that weaken the bones
- Foot deformities or improper footwear
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a foot fracture include:
– Severe pain that increases while walking or standing
- Swelling and bruising
– Tenderness to touch
– Difficulties in walking or bearing weight on the foot
– Deformity or instability of the foot
Diagnosis
Doctors usually start diagnosing foot fractures by asking about the symptoms, the mechanism of injury, and previous medical history. They may perform a physical examination to assess the affected area’s condition. Additionally, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI could be performed for a more detailed view and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for foot fractures can be conservative or surgical, depending on the type and severity of the fracture.
– Conservative treatment: This includes rest, ice, compression and elevation (RICE method). The doctor might immobilize the foot using a cast or boot to facilitate proper healing. Physical therapy can also be beneficial in improving strength and mobility.
– Surgical treatment: In more severe cases, surgery might be needed to realign and secure the broken bones. This could involve the insertion of plates or screws.
Living With Foot Fractures
While recovering from a foot fracture, it’s essential to:
– Rest and elevate the foot as much as possible
– Use crutches or a wheelchair to avoid weight bearing on the affected foot
– Follow your doctor’s instructions on activity level and mobility
– Continue with physical therapy or exercises to regain strength and flexibility
– Eat a balanced diet rich in calcium and Vitamin D for bone health
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
– Severe pain and swelling in the foot
– Difficulty in bearing weight or walking
– Noticeable deformity in the foot shape
– Symptoms that do not improve with conservative treatments
Dealing with a foot fracture can be challenging, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and care, most people fully recover without significant complications.
