Ganglion Cysts
Overview
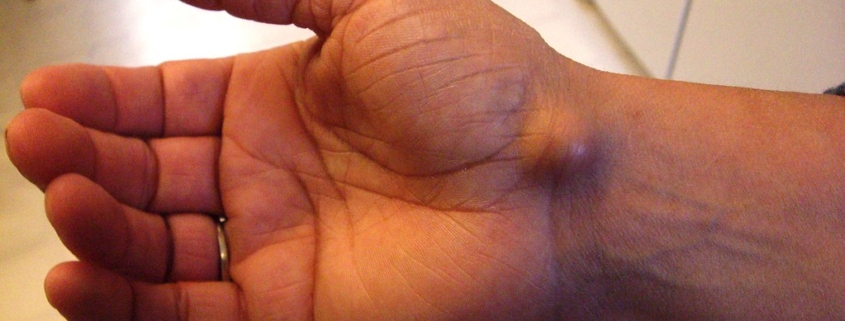
Ganglion Cysts, often referred to simply as ganglia, are benign (non-cancerous) swellings or lumps that typically appear in the hand or wrist, though they can also occur in other parts of the body including the foot or ankle. They are usually round or oval-shaped, filled with a jelly-like substance. Ganglion cysts are quite common, with women and individuals aged 20-40 being more likely to develop them.
Types
Ganglion cysts are often categorized based on their location. The common types include:
-
- Dorsal Wrist Ganglion: This is the most prevalent type, occurring on the back of the wrist.
-
- Volar Wrist Ganglion: These occur on the palm side of the wrist.
-
- Flexor Tendon Sheath Ganglion: Found on the palm side of the fingers, these can also develop on the toes.
-
- Mucous Cyst: This small, fluid-filled cyst appears near the nail bed of your fingers or toes.
Causes
The exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unknown. However, they may arise due to an injury, overuse of a joint, or wear and tear of the surrounding tissue. They tend to be associated with your joints or tendons, suggesting they may be linked to mechanical changes in these areas.
Symptoms
Ganglion cysts often manifest as visible lumps, but symptoms may vary depending on the location of the cyst. Common symptoms include:
-
- A noticeable lump, which can vary in size
-
- Discomfort or pain, especially when the cyst presses against a nerve
-
- Difficulty with movement, particularly when the cyst is in a joint
-
- Tingling or numbness, if the cyst is pressing on a nerve
Diagnosis
A doctor usually diagnoses a ganglion cyst through a physical examination, taking into consideration its shape, size, location, and whether it’s tender to touch. They may also use a light source to see if light passes through the cyst (transillumination), and may aspirate (draw out) fluid from the cyst for analysis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a ganglion cyst can range from non-invasive methods to surgical procedures, depending on the size, location, and symptoms:
-
- Observation: If the cyst is not causing pain or interfering with movement, your doctor might advise waiting and monitoring it for any changes.
-
- Aspiration: This involves using a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst. However, the cyst might recur.
-
- Surgery: If the cyst is causing significant symptoms or interfering with function, surgery to remove the cyst might be an option.
Living With Ganglion Cysts
Living with a ganglion cyst can vary greatly depending on its size and location. Some tips to manage symptoms and cope with the condition include:
-
- Avoiding activities that cause pain or discomfort
-
- Resize rings or watches if they cause discomfort in the concerned area
-
- Wearing supportive wrist guards or foot orthoses, if beneficial
-
- Seek occupational and physical therapy guidance
When to Seek Help
It’s important to see a doctor if you notice any new lump or bump, or if you experience pain or decreased mobility. While ganglion cysts are generally harmless, they may sometimes be confused with other, more serious conditions such as arthritis or cancer. Furthermore, if a previously diagnosed cyst changes in size, is painful, or affects your ability to perform daily tasks, seek medical attention.
