Golfer’s Elbow
Overview
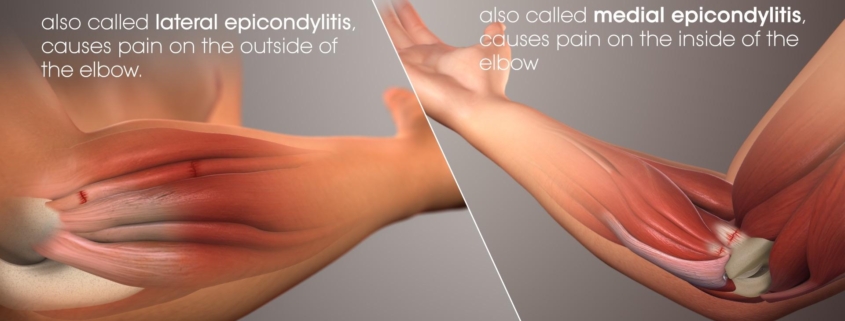
Golfer’s elbow, also known medically as medial epicondylitis, is a condition that causes pain around the inner elbow and forearm area. Despite the name, this disorder affects more than just golfers. Anyone who performs repetitive movements that strain the forearm muscles, like plumbers, cooks, or carpenters can also develop this condition. It is less common than its counterpart, tennis elbow, which affects the outside of the elbow.
Types
Golfer’s elbow is a type of tendinitis, which is inflammation of the tendons. In this case, the tendons involved are those that help control the wrist and fingers. The condition doesn’t have different types or subtypes, but it does vary in severity, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and disability.
Causes
Golfer’s elbow is primarily caused by overuse and strain of the muscles and tendons in the forearm. This can be due to:
-
- Repetitive or forceful wrist and finger motions
-
- Incorrect lifting, throwing, or hitting techniques
-
- Using equipment that is too heavy or with a grip that is too large
-
- Sudden impact, like stopping a fall with the hand
Symptoms
The main symptom of golfer’s elbow is pain and tenderness around the inside of the elbow and the forearm. Other associated symptoms include:
-
- Stiffness in the elbow
-
- Weakness in the hands and wrists
-
- Numbness or tingling, which may radiate into the fingers, typically the ring and little finger.
-
- Pain or discomfort that worsens with certain movements, such as picking up objects with palm down.
Diagnosis
Golfer’s elbow is often diagnosed based on your medical history and a physical examination. Your doctor will apply pressure to the affected area and may ask you to move your elbow, wrist, and fingers in various ways. An X-ray or MRI may be recommended to rule out other causes of elbow pain.
Treatment Options
The main goal of treatment is to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Initial treatment typically includes rest and over the counter pain relievers. Other treatments methods may involve:
-
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can show you exercises to stretch and strengthen your muscles.
-
- Use of a brace: A brace centered over the back of your forearm may help relieve symptoms by resting the muscles and tendons.
-
- Steroid injections: In more severe cases, your doctor may suggest injecting a corticosteroid medication into the painful area to reduce inflammation.
-
- Surgery: If symptoms do not respond to conservative treatments, surgery may be an option. This usually involves removing damaged tissue and reattaching healthy tendon to the bone.
Living With Golfer’s Elbow
Living with golfer’s elbow can mean making some lifestyle changes to help alleviate symptoms. These may include:
-
- Regularly applying ice to the affected area
-
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition
-
- Implementing exercises designed to improve flexibility and strength
-
- Using proper techniques and equipment in sports and other activities to avoid strain
When to Seek Help
A few weeks of home care should alleviate the symptoms of golfer’s elbow. If you are not experiencing relief despite rest and self-care measures, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider. Additionally, if you have severe elbow pain, cannot bend your elbow, or have noticeable swelling, these could indicate a more serious injury and immediate medical attention should be sought.
