Guyon’s Canal Syndrome
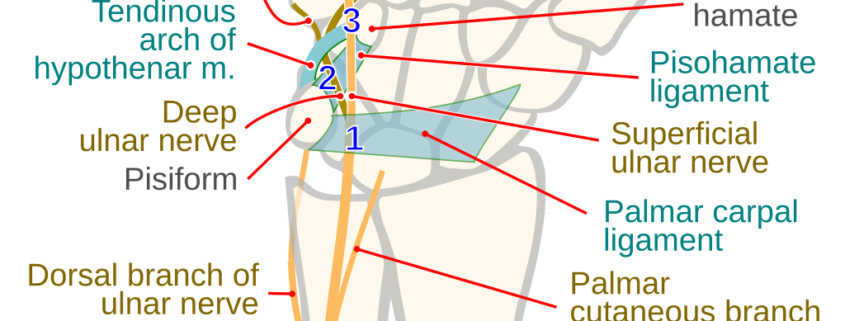
Overview
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome, also known as Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome, is a relatively rare medical condition that affects the hand and wrist. It is specifically caused by compression, trauma, or repetitive injury to the ulnar nerve as it passes through a tunnel in the wrist called Guyon’s Canal. This condition can lead to weakness, numbness, and discomfort in the hand and fingers.
Types
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome comes in three distinct types, each reflecting the part of the ulnar nerve affected:
– Type I: Primarily affects motor functions, leading to muscle weakness, with limited sensory impairment.
– Type II: Primarily impacts sensation in the hand, resulting in numbness or tingling with minimal muscle weakness.
– Type III: Affects both motor and sensory functions, leading to muscle weakness and sensory symptoms.
Causes
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome can stem from a variety of causes:
-
- Constant pressure on the palm, such as in cycling or using crutches
-
- Repetitive hand movements, particularly those that involve twisting or gripping
-
- Direct trauma to the hand or wrist
-
- Tumors, cysts, or inflammation in the wrist area
Symptoms
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
-
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers, particularly in the ring and little fingers
-
- Weakness in hand grip
-
- Pain in the wrist or hand
-
- Difficulty with finger coordination
Diagnosis
If you’re experiencing symptoms of Guyon’s Canal Syndrome, doctors might perform one or several of the following diagnostic procedures:
- Physical Examination: Checking the hand for sensitivity to touch and strength of finger movements
- Nerve Conduction Study: An electric current is used to evaluate the nerve’s ability to send signals
- MRI: This imaging technique can show the exact location and severity of the nerve compression
Treatment Options
Treatment for Guyon’s Canal Syndrome usually starts conservatively, escalating if necessary:
– Conservative Measures: These include rest, wearing a wrist brace, physical therapy, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs.
– Steroid Injections: If conservative measures are not successful, your doctor may recommend a steroid injection to reduce inflammation.
– Surgery: In serious cases, surgery may be required to relieve pressure on the ulnar nerve.
Living With Guyon’s Canal Syndrome
Living with Guyon’s Canal Syndrome can be challenging but manageable. Here are some practical tips:
-
- Take frequent breaks if your job or hobby involves repetitive hand movements
-
- Regularly perform hand and wrist exercises recommended by your physical therapist
-
- Make sure to wear your wrist brace especially during activities that apply pressure to the hand
-
- Speak openly with your doctor about your symptoms and how they are impacting your daily life
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent or worsening signs of Guyon’s Canal Syndrome, seek medical help immediately. Swift intervention can prevent permanent nerve damage and help improve the prognosis. If you notice complete loss of sensation, constant pain, or if your symptoms are impacting your daily activities, it is time to seek professional medical intervention.
Remember, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your health. Early diagnosis and management of Guyon’s Canal Syndrome can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with the condition.
