Hamstring Injuries
Overview of Hamstring Injuries
A hamstring injury refers to strains or tears in the hamstring muscles found at the back of the thigh. These injuries are common amongst athletes, particularly those involved in sports requiring quick starts, such as soccer and track and field. If you’ve had a hamstring injury, you’re more likely to have another one, particularly if you try to get back to high-level physical activity too quickly. Understanding hamstring injuries can help manage the condition effectively and prevent further injuries.
Types of Hamstring Injuries
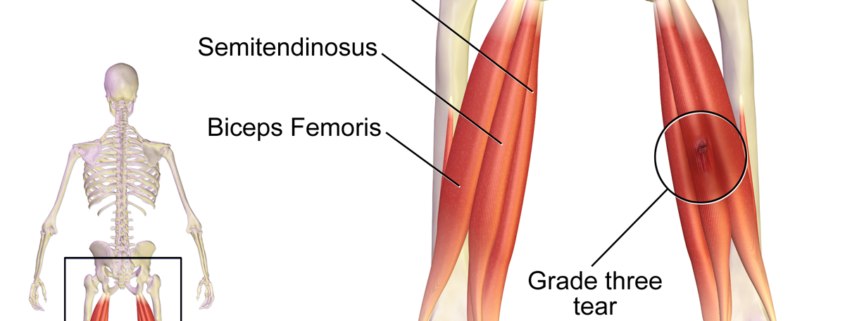
Hamstring injuries typically fall into three categories, each with varying degrees of severity:
-
- Grade 1: A minor muscle pull or strain.
-
- Grade 2: A partial muscle tear.
-
- Grade 3: A complete muscle tear, which may also involve a tendon tear.
The grade of your injury impacts the treatment approach and recovery time.
Causes of Hamstring Injuries
These injuries often occur with sudden, explosive movements such as running or jumping and can result from both underlying conditions and activities. Common risk factors include:
-
- Lack of flexible or strength: Imbalance between the quadriceps and hamstring muscles can increase risk.
-
- Previous injury: An earlier hamstring injury might not have healed completely, making you prone to reinjury.
-
- Age: The risk increases with age owing to declining flexibility and strength.
-
- Sudden increase in amount or intensity of physical activity.
Symptoms of Hamstring Injuries
Common symptoms include:
-
- Sudden, sharp pain in the back of the thigh
-
- Swelling or tenderness
-
- Difficulty walking or running
-
- Feeling of weakness in the hamstring
In severe cases, bruising may appear, and patients may struggle with weight-bearing activities.
Diagnosis of Hamstring Injuries
Doctors typically conduct a physical exam, assessing pain levels when the leg is moved into various positions. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds might also be necessary to determine the extent of the injury.
Treatment Options for Hamstring Injuries
Most hamstring injuries heal with rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy. Treatment usually involves:
-
- RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation
-
- Physical therapy: Exercises to restore strength and flexibility
-
- Surgery: In rare cases, extensive tears may need surgical repair
Living With Hamstring Injuries
Living with a hamstring injury requires a balance of rest, therapy, and potential lifestyle changes. Here are some tips:
-
- Warm up before exercise and cool down after.
-
- Incorporate strength training and stretching into your exercise regimen to strengthen the hamstring muscles and improve flexibility.
-
- Rest adequately to allow the body to recover from physical activity.
-
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to promote muscle recovery.
When to Seek Help
Seek medical attention right away if you experience severe pain, can’t walk, have swelling or bruising in your leg, or if your symptoms don’t improve after a week of self-care. With correct understanding and management, it’s possible to recover from hamstring injuries and gradually return to normal activities. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice based on your health and fitness level.
