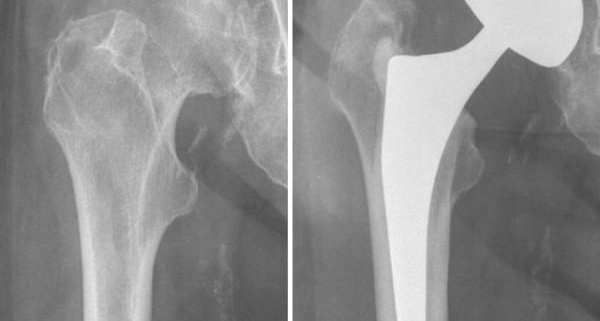
Hemiarthroplasty of the Hip
Overview
Hemiarthroplasty of the hip is a surgical procedure often used to treat severe hip fractures, particularly in older adults. During this surgery, the damaged or diseased portion of the hip joint is replaced with a prosthetic implant, while the healthy portion is left intact. This surgical approach can offer significant benefits, including reduced pain, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of hip hemiarthroplasty, from its causes and symptoms to treatment options and living with this condition.
Types
Hip hemiarthroplasty can be categorized into two types based on the part of the joint being replaced:
-
- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty: In this procedure, both the head of the femur (thighbone) and the natural hip socket remain intact, but a two-part prosthetic device is placed on the femoral head.
-
- Unipolar Hemiarthroplasty: Only the femoral head is replaced with an artificial component, while the hip socket is left unaltered.
Your doctor will decide the best type of hemiarthroplasty based on your bone health, age, lifestyle, and severity of injury.
Causes
Hemiarthroplasty of the hip is usually required due to a severe fracture of the hip joint. These fractures are most commonly caused by:
-
- Falls
-
- Osteoporosis (weakening of the bones)
-
- Traumatic injuries, such as car accidents.
Symptoms
The main symptom that may lead to a hemiarthroplasty is hip pain severe enough that it impairs your ability to walk or perform daily activities. Other symptoms may include:
-
- Decreased range of movement
-
- Swelling or inflammation around the hip
-
- Inability to bear weight on the affected side
Diagnosis
Hemiarthroplasty is typically suggested after a thorough physical examination and diagnostic tests confirm a severe hip fracture. Diagnostic procedures may include:
-
- X-rays
-
- Computed tomography (CT) scans
-
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
These tests provide a detailed picture of your hip joint, helping your doctor identify the extent of the injury and determine the most appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Hemiarthroplasty is a key treatment option for severe hip fractures, particularly in older adults or those who may not tolerate a total hip replacement. Other treatment possibilities may include conservative non-surgical approaches such as traction or wearing a brace, although these methods may not work for everyone or every type of injury.
The hemiarthroplasty procedure typically involves general anesthesia, the use of sterilized surgical instruments, and placement of a prosthetic implant to replace the damaged area of the hip. Rehabilitation typically includes physical therapy, pain management, and exercises to strengthen the hip and enhance mobility.
Living with Hemiarthroplasty of the Hip
Living with a hemiarthroplasty requires care and attention to promote healing and maintain function. Essential considerations include:
-
- Follow the prescribed rehabilitation program: This might involve physiotherapy exercises to promote mobility and strength.
-
- Eat a healthy diet: Proper nutrition helps to repair tissue and maintain overall health.
-
- Keep weight in check: Extra body weight places additional pressure on the hip joint.
-
- Take medications as prescribed: Your doctor may prescribe drugs for pain management and to reduce inflammation.
-
- Use aids if necessary: Assistive devices such as crutches or walkers can help during the early stages of recovery.
When to Seek Help
You must seek immediate medical help if you experience any of the following after hemiarthroplasty:
-
- Persistent or increasing hip pain
-
- Abnormal swelling or redness around the hip
-
- Signs of infection, such as fever or increased pain
-
- Dizziness or shortness of breath
-
- Chest pain
-
- New difficulty moving your hip
Early detection and appropriate management of potential issues are vital to ensure a successful outcome with a hip hemiarthroplasty.
