Hip Replacement
Overview
A hip replacement is a surgical procedure performed to replace a damaged hip joint with an artificial one. It is typically recommended after other treatment methods like physical therapy or medications have failed to relieve chronic hip pain or improve joint function. According to the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, hundreds of thousands of hip replacements are done every year in the United States.
Types
There are two main types of hip replacements:
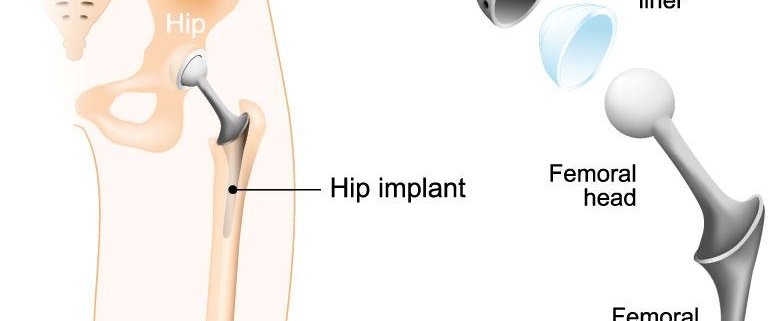
1. Total hip replacement: In this procedure, both the ball and socket of the hip joint are replaced with prosthetics.
2. Partial hip replacement: Only the ball of the hip joint is replaced in this type of surgery.
Causes
Hip replacements are typically caused by the age-related wear and tear of the hip joint, but there are other contributing factors such as:
– Osteoarthritis
– Rheumatoid arthritis
– Hip fractures
– Hip dysplasia
– Avascular necrosis, a condition caused by inadequate blood supply to the ball part of the hip joint
Symptoms
The symptoms indicating the need for a hip replacement include:
– Persistent hip pain that doesn’t go away with rest or medications
– Difficulty walking or performing normal tasks due to hip pain
– Hip pain that worsens with weather changes
– Stiffness in the hip that limits movement
Diagnosis
Your doctor will diagnose the need for a hip replacement based on medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging such as X-rays or MRI scans.
Treatment Options
Before considering surgery, your doctor will likely recommend non-surgical treatment options such as medications, physical therapy, or lifestyle modifications like exercise and weight loss. However, if these methods are unsuccessful, a hip replacement may be considered.
In hip replacement surgery, the damaged part of the hip joint is removed and replaced with artificial parts made of metal, ceramic, or hard plastic.
Living With Hip Replacement
After the surgery, you will undergo a recovery period which typically includes physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the joint. You will need to take medications to manage pain and to prevent complications such as blood clots.
Lifestyle modifications will also be necessary. These can include some or all of the following:
– Regular exercise to maintain strength and flexibility
– Weight management to reduce stress on the joint
– Balanced diet for overall health and faster healing
– Avoiding high-impact activities which may damage your new hip joint.
When to Seek Help
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as:
– Increased or sudden pain in the replaced joint
– Inability to move or put weight on the hip
– Signs of infection like fever, redness, and swelling
Remember, a successful hip replacement largely depends on your active participation in recovery and follow-up care. Make sure to communicate with your healthcare provider about any concerns or issues.
a hip replacement is a common and generally safe procedure that can significantly improve your quality of life if you suffer from a damaged hip joint. However, like any surgery, it comes with risks and requires a commitment to recovery and rehabilitation.
