Hip Tendinitis
Overview
Hip tendinitis, also known as hip tendonitis, is a common but often overlooked condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons in the hip joint. These tendons act as strong bands that connect various hip muscles to the bones, allowing for efficient movement. When exposed to wear and tear or injury, these tendons can become swollen and painful, leading to the condition known as hip tendinitis.
Types
While hip tendinitis is a general term used to describe inflammation of the tendons in the hip, the condition can be distinguished by the specific tendons affected:
1. Gluteal Tendinitis: It affects the gluteal tendons, which link your hip muscles to your pelvis.
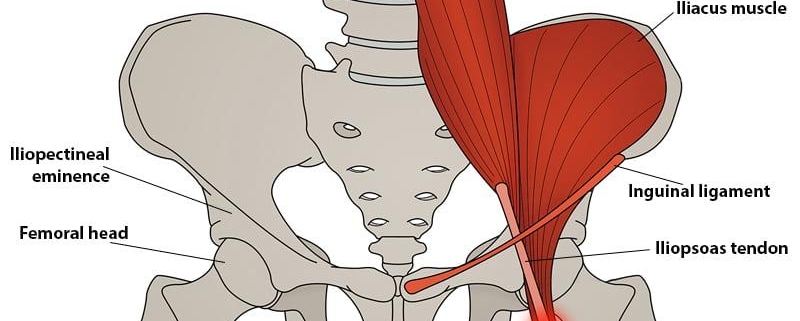
2. Iliopsoas Tendinitis: It affects the iliopsoas tendon, responsible for straightening your hip.
3. Adductor Tendinitis: It targets the adductor tendons, which bring your thighs towards the middle of your body.
Causes
The main cause of hip tendinitis is excessive use or strain of the hip joint. It occurs due to:
1. Repetitive motion or overuse (common in athletes and people with occupations that require recurrent hip movements).
2. Hip injuries.
3. Aging.
4. Obesity, which places extra stress on the tendons.
5. Underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of hip tendinitis include:
1. Persistent pain in the hip that intensifies during activity.
2. Tenderness around the hip area.
3. Stiffness in the hip, especially in the morning.
4. Swelling over the hip.
5. Difficulty in moving or performing regular activities.
Diagnosis
In diagnosing hip tendinitis, healthcare providers generally perform a physical exam and review your medical history. In addition, they may recommend:
1. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds, to visualize the hip joint and surrounding structures.
2. Blood tests to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
Treatment Options
Various treatment options for hip tendinitis include both conservative and surgical approaches:
1. Conservative treatments:
- Rest and avoiding activities that can worsen the symptoms.
- Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility.
– Over-the-counter pain relievers.
– Ice packs to reduce inflammation.
– Corticosteroid injections to relieve pain and inflammation.
2. Surgical treatments: If conservative treatments don’t work, surgery may be recommended to repair the damaged tendon.
Living With Hip Tendinitis
To manage hip tendinitis, one may follow these tips:
1. Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the hip joint.
2. Engage in regular physical exercise to strengthen your hip muscles.
3. Take breaks from repetitive hip movements.
4. Practice good posture at all times to decrease the chances of tendon irritation.
5. Use assistive devices, like a cane or walker, if needed to ease the pressure off your hip.
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical help if you experience:
1. Severe pain and swelling in your hip.
2. A sudden inability to move your hip or bear weight on your leg.
3. Hearing a popping or clicking sound in your hip during a fall or injury.
Remember, early diagnosis and appropriate management of hip tendinitis can lead to a better prognosis and improved quality of life. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider if you suspect you have this condition.
