Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Overview
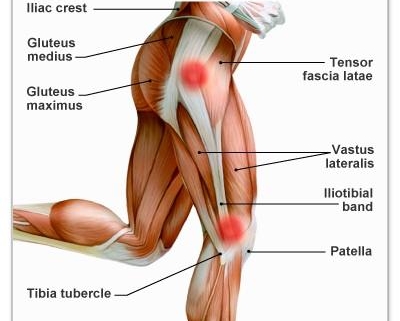
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS) is a common type of knee injury often seen in runners, cyclists, and hiking enthusiasts. The Iliotibial Band, a thick piece of connective tissue, runs from the hip down to the shin. When this tissue becomes inflamed, tight or irritated, it can result in pain and discomfort, generally referred to as ITBS.
Types
Iliotibial Band Syndrome isn’t categorized into types or subtypes. Instead, there is a variability in the severity of the syndrome, ranging from a mild irritation that recedes with rest and proper care to a serious condition requiring substantial medical intervention.
Causes
ITBS can be triggered due to several factors, including:
- Overuse: ITBS often affects individuals who engage in repetitive leg motion, such as running or cycling.
– Incorrect form or technique: Performing physical activities with improper form can put undue stress on the IT band.
– Flat feet: This can result in the knee collapsing inward when running, leading to added tension on the IT band.
– Poor flexibility: Tight muscles can increase tension on the IT band, resulting in inflammation and discomfort.
Symptoms
The most defining symptom of ITBS is a stinging sensation on the outer part of the knee, particularly during or after physical activity. Additional symptoms may include:
– Pain that worsens with continued movement
– Swelling around the knee joint
– A feeling of the knee “locking” or “giving out”
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ITBS typically involves a complete medical history taken by your healthcare provider, a physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI. Specifically, your doctor may perform the Ober’s test to assess the tightness of the IT band.
Treatment Options
The initial treatment for ITBS typically involves conservative approaches including:
– Rest: Reducing or completely stopping the activities that are causing pain can aid in recovery.
– Ice: Applying ice to the sore area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
– Stretching: Exercises to stretch and strengthen the IT band and surrounding muscles can alleviate pain and prevent future injuries.
– Physical Therapy: A specialized therapy program might be beneficial in treating ITBS.
In severe cases, steroidal injections or surgery may be considered. Medications for pain management may also be prescribed.
Living With Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Living with ITBS requires adopting preventive measures that can help manage the condition and prevent flare-ups:
– Regular exercises: Strengthening hip and core muscles can alleviate the stress on the IT band.
– Warm-up and cool down: Before starting any physical activity, adequate warm-up followed by cool down exercises are crucial.
– Modify your routine: If particular activities seem to trigger symptoms, consider approaching them differently.
– Use proper equipment: Ensure that running shoes and sports equipment fit well and are in good condition.
When to Seek Help
Immediate medical attention should be sought if the pain intensifies, interferes with daily activities, or if the following symptoms are present:
– Severe swelling around the knee
– Persistent pain even after rest and at-home remediation
– Difficulty in walking or bearing weight on the affected leg
Remember, early intervention and proper medical guidance are key to managing ITBS effectively. Willingness to take the necessary preventive measures can greatly aid in maintaining an active and pain-free life.
