Knee Ligament Injuries
Overview
Knee ligament injuries are common health conditions that impact the ligaments holding your knee bones together. The ligaments are crucial for knee stability. Strains on these ligaments can lead to injuries which are common among sportspersons, fitness enthusiasts, and even those with physically demanding jobs. By understanding and proactively managing such injuries, you can effectively prevent long-term complications and maintain your mobility.
Types
Knee ligament injuries are usually categorized into four types, based on the affected ligament:
-
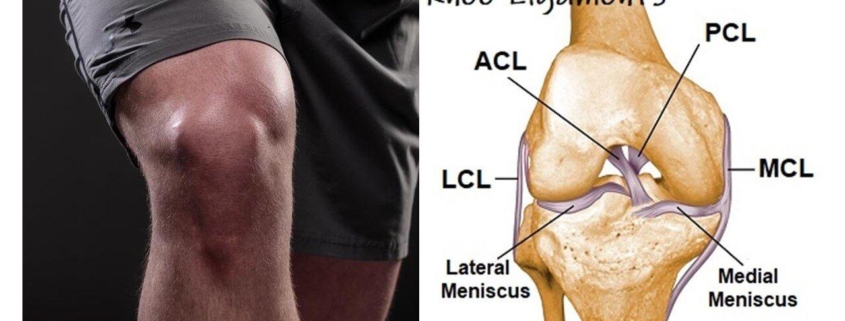
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries: One of the most common and severe types, often occurring due to sudden changes in direction or hard landings.
-
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injuries: Caused by impact to the front of the knee, typically during vehicular accidents or sports injuries.
-
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injuries: Usually due to direct blows to the outer aspect of the knee.
-
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injuries: Occur due to direct forceful impact to the inner side of the knee.
Causes
Knee ligament injuries are typically caused by:
-
- Direct impact, such as a collision during sports or a fall.
-
- Sudden twisting or pivoting of the knee.
-
- Incorrect landing after a jump.
-
- Overextension of the knee joint.
Overuse, obesity, and weak muscle strength can also increase the risk of knee ligament injuries.
Symptoms
Symptoms of knee ligament injuries may vary based on the severity and the affected ligament. Common symptoms include:
-
- Pain and swelling.
-
- Difficulty in bending or straightening the knee.
-
- Instability or feeling of loosening in the knee.
-
- Popping sound at the time of injury.
Diagnosis
Knee ligament injuries are diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, patient’s medical history and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans. Physical tests involve examining the knee by touch and movement. These tests help evaluate the knee’s range of motion, stability and overall functionality.
Treatment Options
Treatment for knee ligament injuries ranges from conservative approaches to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the injury:
-
- Conservative Treatments: Include rest, ice application, compression, elevation (RICE), pain relievers, physiotherapy, and using a knee brace for support.
-
- Surgical Treatments: Are considered when injuries do not respond to conservative treatments, or in case of severe injuries. These may include ligament repair or reconstruction surgery.
Living With Knee Ligament Injuries
Living with a knee ligament injury calls for conscious changes in your lifestyle:
-
- Regularly practice strengthening and stretching exercises to improve knee stability.
-
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on your knees.
-
- Wear supportive footwear and use knee braces if recommended by your doctor.
-
- Take prescribed medication as instructed and ensure proper rest to allow healing.
When to Seek Help
If you experience severe knee pain, swelling, or if your knee feels unstable and is unable to bear your weight, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt intervention can prevent complications and foster a quicker recovery. Remember, when it comes to knee ligament injuries, early detection and appropriate treatment make a substantial difference in your long-term knee health.
