Knee Osteoarthritis
Overview
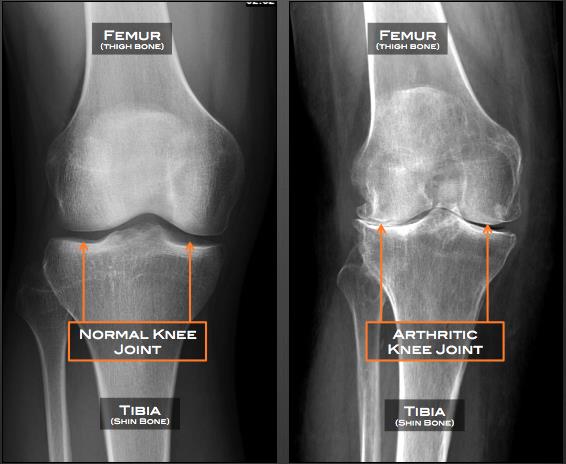
Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) is a medical condition that usually affects individuals middle-aged and older. As one of the most frequent types of arthritis, it involves the breakdown of the cartilage in the knee, leading to pain, stiffness, and mobility challenges.
Types
There are primarily two types of knee osteoarthritis:
-
- Primary OA: This is linked to the aging process and is most common in individuals over 60.
-
- Secondary OA: This often happens at a younger age. It’s developed due to specific risk factors such as obesity, injury, or repeated stress on the knee.
Causes
While the exact origin of knee osteoarthritis is unknown, several factors contribute to its development, including:
-
- Age: The risk increases as one gets older.
-
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop OA.
-
- Weight: Extra weight puts stress on knee joints.
-
- Injury: Any injury to the knee can cause OA.
-
- Genetics: Lonk Knee osteoarthritis can run in families.
Symptoms
The following are common symptoms of knee OA:
-
- Pain during activity
-
- Stiffness or swelling in the knee
-
- Decreased mobility of the knee
-
- Crunching or popping sounds when moving the knee
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, including X-rays and MRI. Your doctor may also order lab tests to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for OA, there are many treatments available to manage symptoms. These can range from lifestyle changes, pain management, to surgery. Treatment options include:
-
- Physiotherapy
-
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatories
-
- Weight maintenance
-
- Exercise, including strength training and flexibility activities
-
- Supportive devices like braces or shoe inserts
-
- In advanced cases, surgery such as knee replacement
Living With Knee Osteoarthritis
Living with OA can be challenging, but it’s important to remember that there are ways to manage your symptoms. Here are some tips:
-
- Pace your activities and take breaks when needed
-
- Use heat or cold packs for temporary relief of pain and inflammation
-
- Stay active, but choose low impact activities
-
- Eat a nutritious diet and maintain a healthy weight
-
- Seek emotional support from family, friends, or a mental health counselor
When to Seek Help
If you notice any of the following, seek medical help immediately:
-
- Inability to move the knee
-
- Increased pain or swelling
-
- Temperature over 100.4 F
-
- New symptoms that were not previously present
