Labral Tears
Overview
Labral tears are a medical condition that involves the cartilage ring (labrum) around the socket (glenoid) of your shoulder or hip joint. The labrum acts as a socket for the ball-shaped head of your humerus (arm bone) or femur (thigh bone) stabilizing the joint and enabling optimal function. When this labrum is torn due to injury, overuse or aging, it can result in pain and decreased function of the affected joint.
Types of Labral Tears
There are primarily two types of labral tears involving different joints:
-
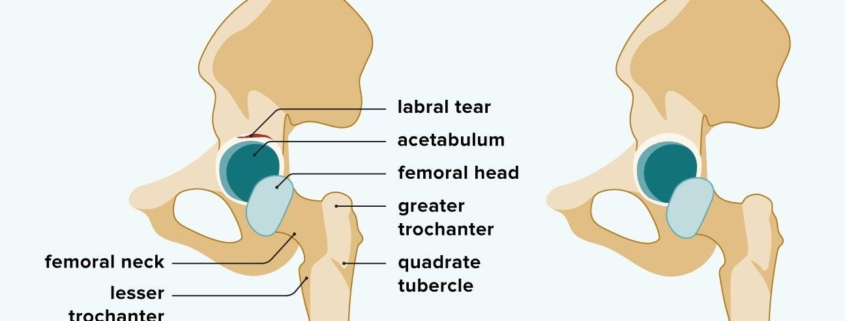
- Hip Labral Tear: This is the tear in the ring of cartilage (labrum) located on the outside rim of your hip joint socket.
-
- Shoulder Labral Tear: This involves the tear in the labrum of your shoulder joint.
Causes of Labral Tears
Labral tears are often the result of trauma or repetitive motion. Here are the main causes:
-
- Trauma: This includes events like a fall, a direct blow to the joint, a sudden lifting of heavy weight, or an accident.
-
- Repetitive motion or overuse: Movements that involve rotation or deep bending of the shoulder or hip can lead to gradual wear and tear of the labrum. This is often seen in athletes who participate in sports like golf, baseball, football, and ballet.
-
- Structural abnormalities: Some people are born with hip conditions that can increase the risk of a labral tear.
-
- Aging: As we age, our body tissues including the labrum can degenerate and weaken, increasing the chance of injury.
Symptoms of Labral Tears
The symptoms of a labral tear often depend on the severity and location of the tear, but commonly include:
-
- Pain, often in the hip or shoulder joint
-
- Clicking, locking, or catching in the joint
-
- Limited range of motion
-
- Feeling of instability in the joint
-
- Decreased strength or function of the joint
Diagnosis of Labral Tears
To diagnose a labral tear, your physician will usually perform a thorough physical examination followed by imaging tests:
-
- Physical examination: It involves checking your range of motion, strength, and joint stability.
-
- MRI scan: This imaging test uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce images of your joint. A special type of MRI called MR arthrography involves injecting dye into the joint to make the labrum more visible.
Treatment Options for Labral Tears
Treatment options usually depend on the severity of the tear and how much it affects your daily life. Treatment typically involves:
-
- Non-Surgical treatment: Initial treatment often includes rest, physical therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and modifying your activities to avoid provoking symptoms.
-
- Surgical treatment: If non-surgical treatments do not relieve your symptoms, your physician might recommend arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive procedure that repairs or debrides the torn labrum. Full recovery often takes several months and includes rehabilitation therapy to restore joint strength and flexibility.
Living With Labral Tears
There are several strategies that can help you manage labral tears:
-
- Physical therapy: Incorporating exercises and stretches into your routine can help in improving joint mobility and stability.
-
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain medications and careful use of ice and heat can help manage pain.
-
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight and adjusting your activities to avoid movements that trigger pain can also help.
When to Seek Help
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
-
- Sudden severe pain in your hip or shoulder
-
- An inability to move your hip or shoulder
-
- Visible deformity or swelling of your hip or shoulder
-
- Persistent pain or symptoms that do not improve with rest and over-the-counter pain medications
Understanding the source of your pain is the first step in finding appropriate treatment. Remember that it’s important to seek medical advice and not ignore your symptoms. The sooner a labral tear is diagnosed, the quicker you can start on the path to recovery.
