Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Overview: Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
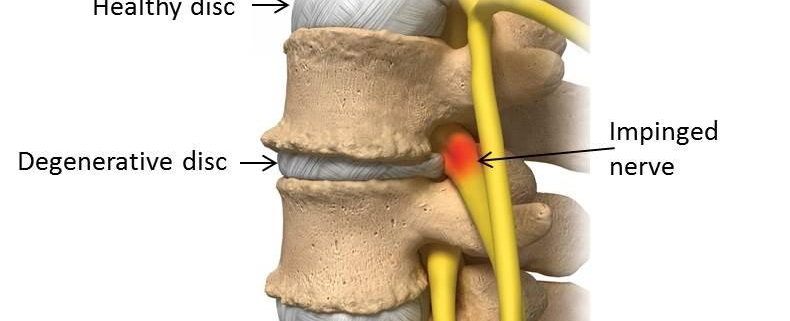
Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease (LDDD) is a common condition that affects the lower back or lumbar spine, often as a part of the natural aging process. It is characterized by the gradual wear and tear of the discs in the spine, leading to discomfort or pain. Millions of individuals worldwide are living with this condition, and it’s most prevalent in people aged 40 and above.
Types of Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
While LDDD is generally considered a single condition, the symptoms and severity can vary greatly among patients. It may manifest as:
– Disc Bulge: The disc remains intact but extends out of its normal place.
– Disc Herniation: The disc’s inner gel-like substance seeps out through cracks in its outer layer.
– Disc Thinning: Also known as disc desiccation, it results from the loss of fluid in the discs, causing them to shrink or thin.
Causes of Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
The primary cause of LDDD is the natural aging process. Over time, the discs in your spine lose hydration, resulting in reduced flexibility and capacity to absorb shock. Other risk factors include:
– Genetic predisposition
– Obesity
– Smoking
– Physical inactivity
– Injury or trauma to the spine
Symptoms Associated with Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
The most common symptom of LDDD is chronic lower back pain, which may worsen with activities like bending, lifting, or twisting. Other symptoms include:
- Intermittent periods of severe pain
- Pain that radiates to the hips, buttocks, or legs
– Difficulty walking or standing
– Stiffness in the lower back
In rare cases, LDDD might lead to numbness or weakness in the legs, signaling nerve involvement.
Diagnosing Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
The first step in diagnosing LDDD is a thorough physical examination and review of medical history by a healthcare professional. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans are often used to visualize the discs and detect any abnormalities. In some cases, a discogram, a procedure that uses a dye injected into the disc followed by an X-ray, might be conducted.
Treatment Options for Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Treatment for LDDD focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Approaches include:
– Conservative Treatments: Physical therapy, pain medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies like acupuncture.
– Interventional Procedures: Epidural steroid injections or nerve root blocks to manage pain.
– Surgery: In severe cases, a lumbar fusion or disc replacement surgery might be recommended.
Living With Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Living with LDDD can be challenging, but proactive self-care can help manage symptoms. Here are some tips:
– Keep Active: Regular physical activity strengthens back muscles and boosts spine support.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight puts additional pressure on your spine. A balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight.
– Use Good Posture: Good ergonomics at work and home can reduce back strain.
– Manage Stress: Techniques like mindfulness and meditation can help manage chronic pain.
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
– Sudden, severe back pain
– Loss of bladder or bowel control
– Progressive weakness or numbness in the legs
Living with LDDD isn’t easy, but a proper understanding and medical guidance can help manage this condition effectively, paving the way for a better quality of life and overall well-being.
