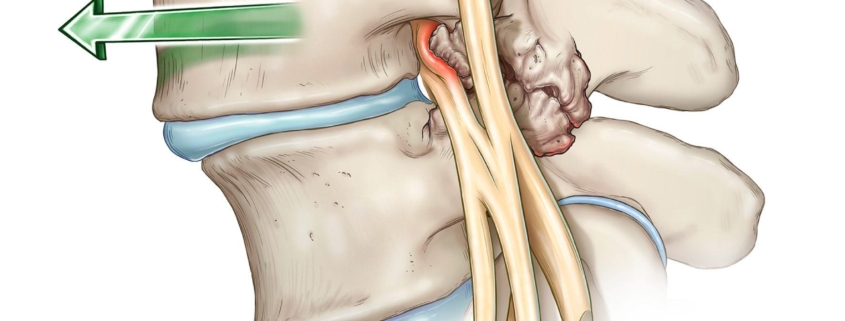
Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Overview of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Lumbar Spondylolisthesis is a medical condition that affects the lower back (lumbar spine) and is often associated with lower back pain and mobility challenges. In simple terms, it’s a situation where one of the vertebrae (bones) in the spine slips forward over the bone beneath it. This condition is quite prevalent, affecting about 5% to 7% of the population, and can affect individuals of all age groups but is more common in adults.
Types of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
There are two primary types of this condition based on the cause.
1. Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: This subtype occurs when there’s a defect in a part of the vertebra called the pars interarticularis. It’s commonly caused by repetitive trauma and is more common in young adults.
2. Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: This type typically occurs due to aging or arthritis. The condition deteriorates the discs and joints in the lumbar spine, making them less able to maintain the alignment of the spinal column.
Causes of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
The primary causes of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis are aging and trauma to the spine. Other risk factors may include:
– Congenital defects (present at birth)
– Arthritis in the spine
– Repetitive stress due to certain activities such as weight lifting or gymnastics
– The presence of certain diseases like bone disorders and tumors.
Symptoms of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
While some individuals may not exhibit any symptoms, others may experience:
– Lower back pain
– Tight hamstring muscles
– Stiffness in the back
– Pain or numbness in one or both thighs
– Difficulty walking or standing for long periods
Diagnosing Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Diagnosis typically begins with a medical history review and physical examination. Doctors may conduct specific maneuvers to pinpoint the source of pain. Imaging tests may also be required, such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
The treatment strategy often depends on the severity of symptoms and the degree of vertebral slippage.
Non-surgical treatments include:
– Physical therapy
– Pain relief medications
– Steroid injections
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to fuse the slipped vertebra(e) to the adjacent bone(s), and in some cases, realign the bones.
Living With Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Managing this condition involves making lifestyle adjustments. These could include:
– Engaging in light exercises that don’t put excessive strain on the back
– Avoiding activities that can worsen symptoms
– Regularly taking prescribed medications
– Undergoing physical therapy to strengthen back muscles
When to Seek Help for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Persons living with this condition should seek immediate medical help if they experience:
– Severe lower back pain that affects mobility
- Numbness or weakness in one or both legs
- Unexplained weight loss
– Fever or chills
Living with Lumbar Spondylolisthesis can be difficult, but with effective management through lifestyle modifications, medication, and therapy, patients can lead a normal, active life. Always consult with a healthcare professional for advice tailored to specific situations.
