Meniscal Injuries
Overview
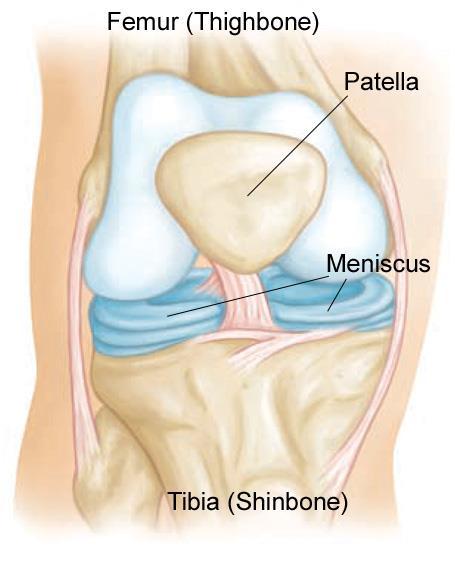
A meniscal injury, also known as a torn meniscus, is a common type of knee injury. Your knee joint consists of three bones, your thigh bone, shin bone, and kneecap. Between your thigh and shin bones are rubbery, C-shaped pieces of cartilage called the menisci. Meniscal injuries typically occur when these pieces of cartilage tear. These tears can happen during activities that involve twisting, pivoting, or being tackled. Such injuries are especially prevalent in athletes but can also affect non-athletes alike.
Types
Meniscal tears are classified into different types based on their appearance and location:
1. Longitudinal tear: A tear running lengthwise along the meniscus.
2. Bucket-handle tear: This is a longitudinal tear that flips, resembling a bucket handle.
3. Radial tear: A tear that starts in the middle of the meniscus and extends to the outer edge.
4. Complex tear: This type has a combination of tear patterns and is commonly seen in degenerative conditions.
Causes
Meniscal tears often occur during activities that put pressure and forcefully rotate the knee. Some common causes are:
– Sports-related activities: Abrupt twisting or turning, sudden stops and starts, direct contact during sports like football and basketball can all lead to meniscal injuries.
– Age-related degeneration: As you age, your menisci wear down, thus increasing the likelihood of tears.
Symptoms
Some common symptoms of a torn meniscus include:
– Pain in the knee
– Swelling or stiffness
– A sensation of your knee giving way
- Inability to move your knee through its full range of motion
– The feeling of the knee ”locking” or getting stuck
Diagnosis
To diagnose a meniscal injury, your healthcare provider could:
– Perform a physical examination of your knee
– Use imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI scan, to visualize the tear
– In some cases, an arthroscopy may be used to get a detailed look at the inside of the knee
Treatment Options
The treatment for meniscal tears depends on the size, type, and location of the tear. Options can range from non-surgical to surgical interventions:
– Non-surgical treatment: If the tear is small and on the outer edge of the meniscus, it could likely heal on its own with rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
– Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen and stabilize your knee can also help in treating non-severe cases.
– Surgery: If the tear is large or causing significant symptoms, like persistent pain or movement issues, arthroscopic surgery might be necessary.
Living With Meniscal Injuries
Successfully managing life after a meniscal injury can involve:
– Attending regular Physiotherapy sessions
– Regularly doing exercises advised by your physiotherapist to regain full knee function
– Maintaining a healthy diet and weight to reduce strain on your knees
– Protecting your knee from further injuries by wearing suitable knee support when doing high-risk activities
When to Seek Help
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience:
– Severe knee pain
- An inability to move your knee normally
– Persistent discomfort or swelling around the knee
Remember that timely intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and the healing process of meniscal injuries. Your healthcare provider should be your primary source of information and guidance in the treatment of any health condition.
