Olecranon Bursitis
Overview
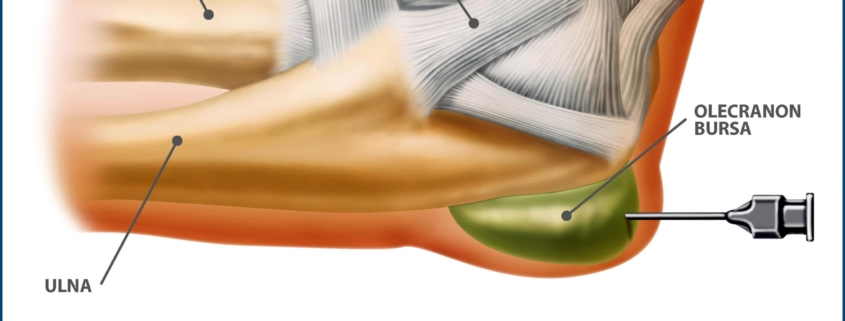
Whether you’re newly diagnosed with Olecranon Bursitis or just seeking more information about this condition, it’s essential to grasp the concept clearly. Olecranon Bursitis, commonly referred to as “elbow bump” or “Popeye elbow”, is a condition characterized by inflammation, pain, and swelling in the bursa, a small, fluid-filled sac that cushions the bony tip in your elbow known as the olecranon. It is a prevalent condition and can affect individuals across all age groups.
Types
Olecranon Bursitis can be divided into two main types: septic and non-septic.
1. Septic Olecranon Bursitis: This type is caused by an infection due to bacteria, leading to inflammation and swelling.
2. Non-septic Olecranon Bursitis: This type is typically caused by injury or trauma to the elbow without the involvement of any infection.
Causes
Several underlying factors can trigger Olecranon Bursitis. These include:
• Direct trauma or blow to the elbow
• Persistent pressure on the elbow such as leaning on a hard surface for extended periods—often seen in students and professionals who work at a desk
• Certain medical conditions like arthritis, gout, or kidney disease can also contribute to its development
• In rare instances, bacterial infections can cause septic olecranon bursitis
Symptoms
The symptoms of Olecranon Bursitis may vary depending on the severity of the case and the type (septic or non-septic). Major symptoms to watch out for include:
• Pain and tenderness at the back of the elbow
• Swelling in the elbow that may limit range of motion
• In more severe cases, fever or the presence of pus, indicating a bacterial infection
Diagnosis
A doctor will usually diagnose Olecranon Bursitis based on a physical examination and medical history. If inflammation and swelling are present, they may recommend further tests such as:
• X-ray: To rule out bone injuries or arthritis
• Aspiration: A procedure to remove fluid from the bursa for testing
• Blood tests: To identify possible signs of infection or gout
Treatment Options
The treatment of Olecranon Bursitis generally centers on reducing pain and inflammation. Here are some common options:
• Non-Surgical Treatments: Involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, elbow padding, and avoiding activities that cause pressure on the elbow
• Aspiration: Excess fluid is drained from the bursa using a syringe
• Steroid Injections: Can be administered for severe cases to reduce inflammation
• Surgical Intervention: Required in rare cases where non-surgical treatments don’t help
Living With Olecranon Bursitis
Living with Olecranon Bursitis can be a challenge, but here are some helpful tips:
• Regularly apply ice to the elbow to reduce swelling
• Use elbow pads to protect the area from further damage
• Carefully follow your doctor’s recommended medication regimen
• Incorporate gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to maintain elbow mobility
• Maintain a healthy weight to avoid putting extra stress on your joints
When to Seek Help
Olecranon Bursitis could gradually improve over time with non-operative treatments. However, if you notice any of the following, consider seeking immediate medical attention:
• Unmanageable pain
• Rapid increase in swelling
• Fever, redness, or warmth over the elbow area, potentially indicating an infection
• Difficulty in moving the elbow
• If non-surgical treatments don’t bring relief
Remember, regardless of the health issue, early diagnosis and treatment often lead to the best outcomes.
