Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Overview of Osgood-Schlatter Disease
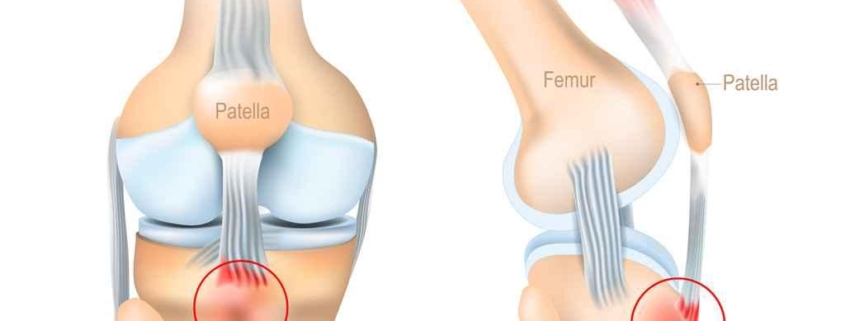
Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) is a common condition affecting children and adolescents, especially those who participate in sports. It occurs when the growing part of the kneecap (the tibial tubercle) becomes inflamed, leading to pain and swelling. This condition prominently affects individuals who are pleasure-seekers of running, jumping, or swift knee-bending activities. Although OSD can be painful, it’s typically temporary and doesn’t cause lasting damage.
Types of Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter Disease isn’t classified into distinct types, but its severity can vary from person to person. Some might experience mild pain only during regular activities, while others may feel persistent, debilitating pain that interferes with their daily routines.
Causes of Osgood-Schlatter Disease
OSD is mostly seen in kids undergoing growth spurts during puberty. During this time, the bones, muscles, and tendons are changing and growing rapidly, sometimes unevenly. If your child’s thigh muscle pulls on the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone, it can result in OSD. This is especially prevalent in high-impact activities like running and jumping, making active kids more susceptible.
Symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Common symptoms of OSD include:
-
- Knee pain and tenderness at the tibial tubercle (bony part where the kneecap meets the shin)
-
- Swelling in the area around the knee
-
- Pain that worsens during activities and eases with rest
-
- Limping after physical exertion
Some children may experience these symptoms in both knees, and in less common cases, a bony lump may appear on the affected knee that persists into adulthood.
Diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter Disease
OSD can usually be diagnosed based on a physical examination and the patient’s symptoms. Occasionally, an X-ray might be ordered to rule out other conditions. During the physical examination, the doctor will apply pressure on the knee to check for pain, swelling, and tenderness.
Treatment Options for Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Typically, OSD can be managed at home with simple remedies like rest, icing the knee, and over-the-counter pain relievers. However, in severe cases, physical therapy may be needed to strengthen the muscles and improve knee movement. In exceptionally rare situations, surgery might be recommended to remove a bony fragment or fix the tibial tubercle.
Living With Osgood-Schlatter Disease
While living with OSD can be challenging, particularly for active kids, the following tips can help manage the condition:
-
- Keep a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
-
- Participate in gentle exercises, like swimming, to maintain fitness without stressing the knee.
-
- Wear a knee pad for protection during physical activities.
-
- Take regular breaks during activity to rest the knee.
When to Seek Help for Osgood-Schlatter Disease
While OSD usually resolves itself with time, immediate medical attention should be sought if your child experiences severe knee pain, inability to bear weight on the affected leg, or noticeable knee joint deformity. A health professional should be consulted if the symptoms persist beyond the growth spurt period, as this might imply another underlying condition.
