Osteoarthritis
Overview
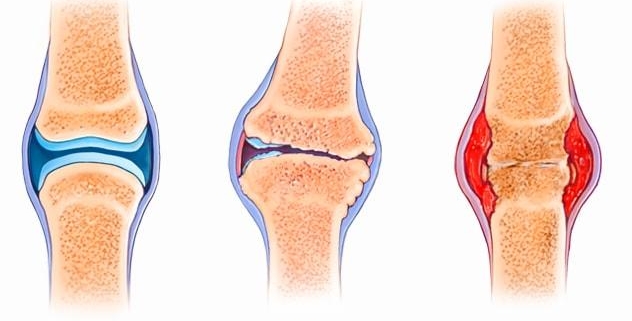
Osteoarthritis, informally known as wear-and-tear arthritis, is a common chronic condition of the joints. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in your joints gradually erodes. This degenerative joint disease affects millions of people worldwide, making it one of the most prevalent forms of arthritis. As osteoarthritis progresses, it can result in severe joint pain and limit mobility, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life.
Types
Osteoarthritis can be classified into two categories: primary and secondary. The former is typically associated with aging and is attributed to the natural wear and tear of the joints. On the other hand, secondary osteoarthritis is caused by an underlying condition or disease, such as obesity or injury, that damages the cartilage.
Causes
While the exact cause of osteoarthritis is unknown, several risk factors contribute to its development. These include:
– Aging: The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age.
– Sex: Women are more likely to develop this condition than men.
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of osteoarthritis are at a higher risk.
– Overweight: Extra body weight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints, increasing wear and tear.
– Joint injuries: Damage from physical activity or an accident can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
– Certain occupations: Jobs that require repetitive stress on a particular joint may lead to osteoarthritis in that joint.
– Bone deformities: Some people may be born with malformed joints or defective cartilage.
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis symptoms often develop slowly and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
– Joint pain during or after movement
– Tenderness when light pressure is applied to the joint
– Stiffness, particularly upon waking up or after being inactive
– Loss of flexibility in a joint
– Grating sensation or cracking sound when a joint is used
– Bone spurs, which are extra bits of bone that form around the affected joint
– Swelling in a joint
Diagnosis
Diagnosing osteoarthritis involves a physical exam, medical history evaluation, and potentially diagnostic tests. The doctor will likely:
– Check joints for tenderness, swelling, redness, and flexibility
– Ask about your symptoms and medical history
– Order imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to see joint damage
– In some cases, the doctor may recommend a blood test or joint fluid analysis to rule out other types of arthritis.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options include:
– Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or prescription medications may help alleviate pain.
– Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen muscles around the affected joint, improving mobility and easing pain.
– Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and other healthy habits can help manage symptoms and prevent disease progression.
– Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures like joint replacement or joint fusion may be necessary.
Living With Osteoarthritis
Living with osteoarthritis can be challenging, but various strategies can help manage the condition:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps maintain joint flexibility and strengthen the muscles that support joints.
– Weight management: Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, so maintaining a healthy weight is crucial.
– Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat or cold to stiff or sore joints can provide relief.
– Assistive devices: Canes, shoe inserts, or other devices can help reduce pain during daily activities.
When to Seek Help
You should seek medical attention if you have persistent discomfort and swelling in your joints, pain that becomes worse over time, or joint symptoms that affect your quality of life. Early diagnosing and managing osteoarthritis can help preserve joint health and improve your daily life. So don’t delay in seeking help if you’re experiencing any of these symptoms.
