Patellofemoral Problems
Overview
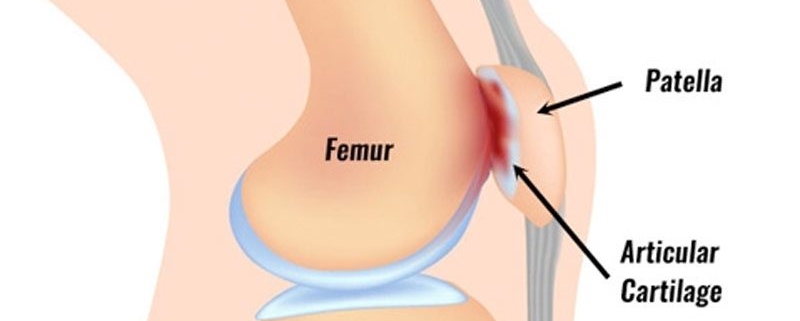
Patellofemoral problems refer to a range of issues that affect the patella (knee cap) and its alignment with the femur (thigh bone). These issues often result in knee pain, discomfort, and limited movement. You’re not alone if you’re dealing with this condition, as it affects a vast number of people worldwide, irrespective of age and gender.
Types
Major types of patellofemoral problems fall into three categories:
-
- Patellofemoral malalignment: This occurs when the kneecap isn’t properly aligned, causing friction with the femur.
-
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS): Also known as runner’s knee, this syndrome is a broad term used to describe pain in the front of the knee and around the kneecap.
-
- Patellar tendinitis: This problem involves inflammation or injury to the tendon that connects the kneecap to your shinbone. It’s commonly seen in athletes who frequently jump.
Causes
Certain factors can predispose you to patellofemoral problems:
-
- Overuse of the knee through repetitive bending activities such as jumping, running, or squatting can lead to kneecap injuries.
-
- Weak or imbalanced thigh muscles may fail to keep your kneecap properly aligned.
-
- Structural abnormalities, trauma or improper shoe gear can result in these knee problems.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of patellofemoral problems include:
-
- Pain in the front of the knee – especially when sitting for long periods or when kneeling, squatting, or using stairs.
-
- A clicking or popping sound in the knee particularly when standing up from a seated position or during physical activities.
-
- Feelings of instability or like the knee may give out.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of patellofemoral problems can involve a number of steps:
-
- The doctor will begin by asking about your symptoms and medical history.
-
- A physical examination will be conducted to assess pain levels and range of knee motion.
-
- Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be used to visually evaluate knee structure and alignment.
Treatment Options
Treatment approaches will generally seek to minimize pain and inflammation, improve knee alignment, and enhance flexibility and strength. These could include:
-
- Physical therapy focusing on strengthening thigh muscles to improve kneecap alignment
-
- Medications to manage pain and inflammation
-
- Use of knee braces or tape for support
-
- In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to repair or realign the kneecap.
Living With Patellofemoral Problems
Living with patellofemoral problems may seem overwhelming, but the following tips could help you manage the condition effectively:
-
- Strengthen your knee and leg muscles through physiotherapy and regular exercise.
-
- Rest your knee and avoid activities that exacerbate pain.
-
- Apply ice packs to your knee to help reduce inflammation and pain.
-
- Use over-the-counter pain relief medications as advised by your healthcare provider.
-
- Wear shoes that provide good support.
When to Seek Help
While patellofemoral problems can often be managed at home, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention if you:
-
- Experience severe pain or swelling in the knee
-
- Can’t straighten the knee or put weight on it
-
- Feel a popping sensation and immediate pain in the knee
-
- See obvious deformity in the leg or knee
While patellofemoral problems might be a common cause of knee pain, proper diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan can effectively manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. Remember, it’s always okay to reach out to your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions.
