Peroneal Tendon
Overview
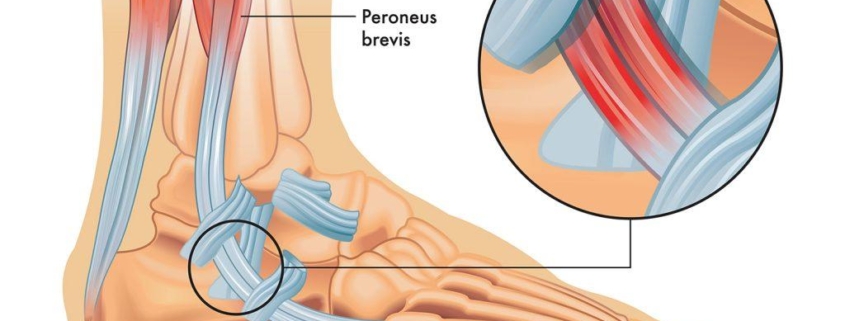
The peroneal tendons are two fibrous cords located on the outer part of the lower leg that attach the peroneal muscles to the foot bone, playing a critical role in our ability to walk, run, and balance. These tendons can become inflamed, torn, or dislocated due to various causes, leading to a condition called peroneal tendonitis. This condition can cause significant discomfort and disrupt normal movement. While peroneal tendon issues are relatively common, awareness is often low until an individual experiences symptoms.
Types
There are mainly two types of peroneal tendon injuries:
1. Peroneal Tendonitis: This occurs when the tendons become inflamed from overuse or an injury.
2. Peroneal Tendon Dislocation/Dysfunction: This happens when one or both tendons slip out of place, often due to a pre-existing genetic condition or a severe injury.
Causes
Most peroneal tendon injuries are caused by activities that put repetitive stress on the tendons, like running or jumping. Other causes include improper footwear, lack of proper warm-up before exercises, a sudden increase in activity intensity, unsuitable surfaces for athletic activities, and accidents or direct blows to the outside of the ankle or foot.
Symptoms
Symptoms of peroneal tendonitis may vary but typically include:
• Pain on the outside of foot or ankle
• Swelling or warmth in the foot or ankle
• A sensation of ankle instability
• Difficulty in weight-bearing activity like walking or standing
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of peroneal tendonitis is made based on your symptoms, a physical examination, and your medical history. Your doctor may also order imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound to get a clearer view of the tendons and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for peroneal tendonitis aims to reduce pain and inflammation and restore function. Options include:
-
- Rest
-
- Ice
-
- Compression
-
- Elevation
-
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
- Physical therapy
-
- Surgery (in severe cases)
Living With Peroneal Tendon
Living with peroneal tendonitis requires adopting strategies to manage pain and prevent future injuries. These might include:
-
- Maintain a healthy weight to minimize stress on your tendons
-
- Warm-up properly before exercises
-
- Wear supportive shoes
-
- Follow your doctor’s advice about physical therapy exercises
You may also need to take NSAIDs or use ice packs to manage pain, or use crutches to reduce weight on your foot while it heals.
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent pain, swelling, redness, warmth or instability in your foot or ankle, it’s important to seek medical help. If left untreated, peroneal tendonitis can lead to chronic instability of the ankle, increasing the risk for repeated sprains and other injuries. Make sure to seek immediate medical care if you have intense pain, cannot put weight on your foot, or your foot is deformed or severely swollen, as these may be signs of a severe injury.
