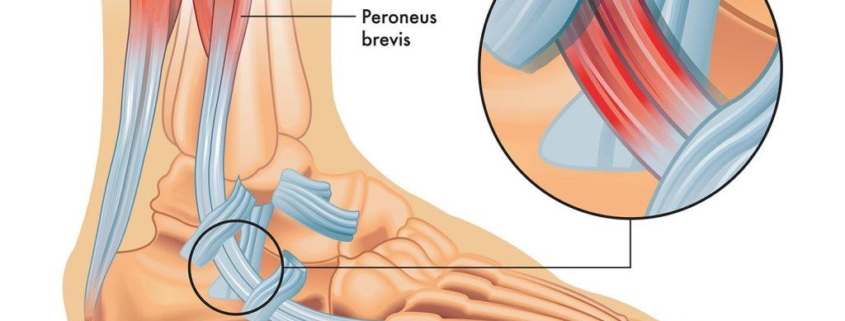
Peroneal Tendon Subluxation
Overview
Peroneal Tendon Subluxation, sometimes referred to as Peroneal Tendon Dislocation, is a condition that affects the foot and ankle. It occurs when one or both of the peroneal tendons (bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones) in the ankle dislocates from their normal position. This condition may result in pain, instability, and a snapping sensation in the ankle. Although it’s not extremely common, athletes involved in high-impact sports like soccer or running are at a higher risk.
Types
Peroneal Tendon Subluxation is primarily divided into two categories:
-
- Acute Subluxation: This is often an immediate outcome of an ankle injury or trauma. It involves a sudden dislocation of the peroneal tendon.
-
- Chronic Subluxation: This happens gradually over time, due to recurring dislocation or instability of the ankle.
Causes
Peroneal Tendon Subluxation is caused by factors that lead to the dislocation of the peroneal tendon from its groove along the fibula bone. Key causes include:
-
- Severe ankle sprain
-
- High-impact activities such as jumping or running
-
- Structural anomalies in the foot or ankle
-
- Weakness in the surrounding ligaments or tendons
Symptoms
The symptoms of Peroneal Tendon Subluxation can vary depending on the severity and type. Common symptoms include:
-
- A snapping or popping sensation in the ankle
-
- Pain and swelling around the outside of the ankle
-
- Difficulty walking or putting weight on the foot
-
- Instability in the ankle
Less common symptoms may include ankle stiffness or limited range of motion in the foot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Peroneal Tendon Subluxation typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests. Your doctor may test the ability of your foot and ankle to move in different directions and will look for signs of swelling, instability, and pain during movement. You may undergo X-Rays, MRI, or Ultrasound to have a detailed view of the bones, tendons, and ligaments in your ankle.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Peroneal Tendon Subluxation often depends on whether the condition is acute or chronic.
1. Non-surgical treatments: These are usually the first steps and may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE method). Immobilization of the ankle using a brace or cast can also help. Physical therapy exercises to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility are also beneficial.
2. Surgical treatments: If non-surgical treatments are not effective, surgery may be recommended. Procedures may involve deepening the groove that the peroneal tendon slides through, repairing the retinaculum (a band of tissue holding the tendons in place), or even rerouting the tendons.
Living with Peroneal Tendon Subluxation
Here are some tips for managing Peroneal Tendon Subluxation:
-
- Follow your physical therapy routine religiously to strengthen the peroneal tendons and prevent further injury.
-
- Wear ankle braces or supportive footwear, especially while playing sports or doing high-impact activities.
-
- Maintain a healthy diet to support bone and tissue health.
-
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by your doctor to manage pain.
When to Seek Help
You should seek immediate medical attention if you suffer a severe injury to your foot or ankle, or if you experience a sudden, severe pain combined with a snapping sensation in the ankle. Also, if you notice a visible deformity in your ankle, or cannot bear weight on your foot, professional medical attention is necessary. If you’ve been diagnosed with Peroneal Tendon Subluxation, and your symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment, contact your healthcare provider promptly.
