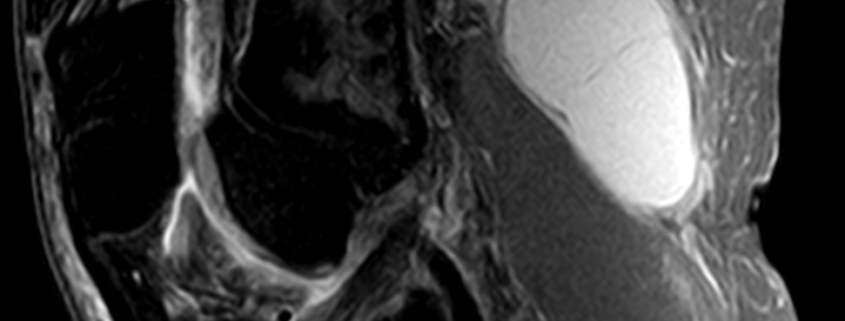
Popliteal Cysts
Overview
Popliteal cysts, commonly known as Baker’s cysts, are fluid-filled sacs that occur in the popliteal fossa, the area behind the knee. These cysts can cause discomfort and restrict movement. They’re most common in people over 40, but they can occur at any age, even in children.
Types
While Baker’s cysts are typically categorized as one condition, they can occur in two types - primary and secondary.
Primary cysts typically occur in children and are not associated with joint or tendon diseases. On the other hand, secondary cysts are often connected with knee disorders such as arthritis or a meniscus tear and are prevalent in adults.
Causes
Popliteal cysts arise from excess fluid in the knee joint. This fluid, known as synovial fluid, is essential for the smooth functioning of your knee joints, but over-production leads to the formation of Baker’s cysts. Causes of excess fluid include:
* Inflammation of the knee joint, which may be due to arthritis or a knee injury
* Damage to the knee’s cartilage, such as a torn meniscus
Symptoms
Many people with popliteal cysts do not experience symptoms. However, some may notice:
* Mild to severe knee pain
* Swelling behind the knee, which may get worse when standing
* The feeling of tightness or stiffness in the knees
* Difficulty bending or fully extending the knee
Diagnosis
Your doctor may be able to diagnose a popliteal cyst by examining your knee. They may also use imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, for a more detailed view of the joint. In some cases, a cyst may be aspirated – a procedure involving drawing fluid from the cyst with a needle for examination.
Treatment Options
Treatment for popliteal cysts often focuses on addressing the underlying conditions causing the excess fluid. This could involve:
* Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation
* Physical therapy to improve joint function
* Steroid injections to reduce inflammation
* Needle aspiration to drain fluid
* Surgery, though only in severe cases where the cyst causes considerable discomfort or complications
Living With Popliteal Cysts
Living with a popliteal cyst can be manageable with some care. Here are some tips:
* Regular exercise: Keeping active helps maintain joint flexibility. Low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling are generally beneficial.
* Rest: When your knee is swollen or painful, take a break. Resting your knee can help reduce inflammation.
* Use of cold packs: Applying a cold pack to the affected area several times a day can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
When to Seek Help
If you notice persistent swelling or discomfort behind your knee, consult a doctor. Additionally, seek immediate medical attention if you encounter symptoms such as:
* Severe swelling and pain in your knee
* Redness, warmth, and tenderness around the affected area
* Difficulty walking or moving your leg
* Suuden worsening of symptoms
Living with popliteal cysts can be a challenge. But with knowledge about the condition and the right care, you can lead an active, healthy life. Remember to follow your healthcare provider’s advice closely and maintain regular check-ups.
