Prepatellar Bursitis
Overview
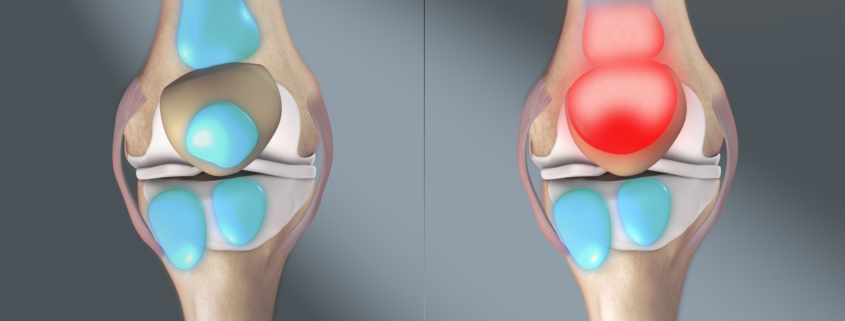
Prepatellar bursitis, often referred to as “housemaid’s knee,” is a common condition that affects the bursa, a fluid-filled sac located in front of your kneecap (patella). The bursa aids in reducing friction between your skin and knee bone. However, when it becomes inflamed, it results in a condition known as prepatellar bursitis.
Types
Primarily, there are two types of prepatellar bursitis:
1. Septic Prepatellar Bursitis: This occurs when bacteria infect the bursa leading to swelling and pain. A wound mechanism is usually the cause of this type of bursitis.
2. Nonseptic Prepatellar Bursitis: This results from constant pressure or friction on the knee, typically from kneeling for long periods.
Causes
Prepatellar bursitis is often caused by:
– Constant kneeling, which puts pressure on the bursa.
– Direct blow to the knee.
- Bacterial infection of the bursa.
– Certain professions involving lots of kneeling such as carpet fitting, gardening, or roofing.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of prepatellar bursitis include:
- Swelling or puffiness at the front of the knee.
– Pain in the knee, particularly when kneeling.
– Tenderness and warmth over the knee.
– Difficulty bending the knee.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis starts with a physical examination of the knee. Your healthcare provider may also:
– Obtain your medical history.
– Perform an aspiration, where fluid is removed from the knee for testing.
– Use imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasound or MRI to confirm diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for prepatellar bursitis often depends on severity and type.
– Conservative treatments include rest, ice, elevation, knee padding, anti-inflammatory medication, and possibly physical therapy.
– Septic Bursitis is typically treated with antibiotics. In more severe cases, the bursa might need to be drained or surgically removed.
– Non-septic Bursitis: If symptoms persist despite conservative measures, a corticosteroid injection may be used.
– Surgery is only considered when all other treatments have failed.
Living With Prepatellar Bursitis
Here are some practical tips for managing prepatellar bursitis:
– Rest and avoid activities that cause knee pain.
– Use ice packs on your knee for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
– Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on your knee.
– If your job involves kneeling, use knee pads.
– Regularly exercise to strengthen your knee muscles.
– Take over-the-counter pain relievers as directed by your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical help if:
– You are unable to move your knee.
– Your knee pain is severe and sudden.
– Your knee swells suddenly.
– You have a fever alongside your knee pain.
– The skin around your knee turns red or feels hot to touch.
– You have difficulty bearing weight on your knee.
Remember timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help you manage prepatellar bursitis efficiently and resume your regular activities sooner. Never hesitate to seek professional help when your symptoms persist or worsen.
