Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Overview: Understanding Radial Tunnel Syndrome
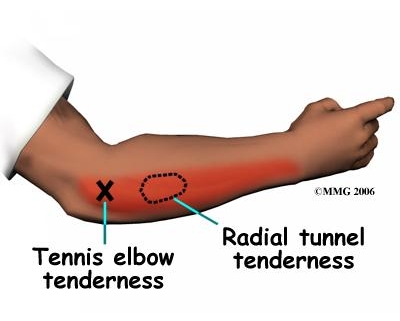
Radial Tunnel Syndrome (RTS) is a condition that affects the radial nerve in the arm. The radial nerve runs down the back of your arm and controls the movement of your triceps (the muscle at the back of the upper arm), wrist, and fingers. When this nerve becomes compressed or irritated, typically around the elbow, it causes the pain and discomfort known as radial tunnel syndrome.
This condition is relatively rare, but it can significantly impact a person’s daily life due to the discomfort and reduced mobility it may cause.
Types: Subtypes of Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Radial Tunnel Syndrome predominantly affects the radial nerve; however, the severity, type, and location of the pain can vary, leading to different subtypes of the condition.
Causes: What Factors Lead to Radial Tunnel Syndrome?
Radial Tunnel Syndrome often occurs as a result of overuse of the arm and hand, especially in activities that involve repetitive wrist or arm movement, such as typing or using certain tools. It can also be caused by direct trauma to the arm or elbow.
Symptoms: Identifying Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Common Symptoms associated with Radial Tunnel Syndrome include:
-
- Persistent, dull ache in the forearm
-
- Pain at the top of the forearm or back of the hand, often worsening with activity
-
- Weakness in the forearm and hand
-
- Difficulty extending the arm or hand fully
In some cases, symptoms may worsen at night or cause discomfort during regular activities such as turning a doorknob or holding a cup.
Diagnosis: How is Radial Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed?
To diagnose Radial Tunnel Syndrome, a doctor or physiotherapist typically performs a combination of physical examination, review of medical history, and possibly imaging tests, like an MRI or X-ray.
Treatment Options: Exploring Cures for Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment for Radial Tunnel Syndrome can vary based on the severity of your symptoms. Some of the strategies may include:
-
- Physical therapy exercises to strengthen and stretch the muscles surrounding the radial nerve.
-
- Medications such as anti-inflammatories and pain relievers to reduce swelling and pain.
-
- Rest and temporary elbow immobilization to allow the nerve to heal.
-
- In severe cases, surgical decompression of the radial nerve may be required.
Living With Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Living with Radial Tunnel Syndrome can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can manage your symptoms and lead an active life. Here are some tips to help manage your condition:
-
- Perform regular exercises and stretches recommended by your physiotherapist.
-
- Avoid activities that require repetitive motion of the arm or hand.
-
- Ensure regular breaks when performing activities that involve the arm and hand.
-
- Use assistive devices or ergonomic equipment to ease pressure on the radial nerve.
-
- Manage your pain with the prescribed medication and hot or cold therapy.
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent pain, numbness, weakness, or if your symptoms worsen, seek medical attention immediately. These could be signs of a more serious condition and may require specialized treatment.
Remember that with the right knowledge and understanding, managing Radial Tunnel Syndrome can be achievable. Always communicate with your healthcare provider, follow their advice, and don’t hesitate to ask questions about your condition and treatment.
