Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Overview
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty, or RSA, is a type of surgery designed to treat a number of shoulder conditions and injuries that cause chronic pain and impair daily functioning. This procedure, also referred to as reverse total shoulder replacement, is often recommended for individuals who have not found adequate relief from non-surgical treatment options.
Types
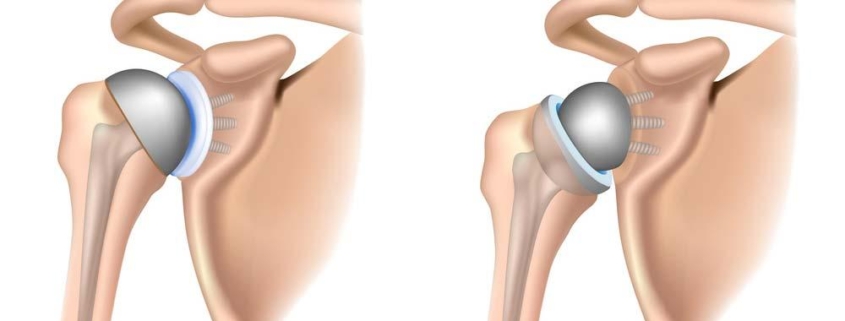
The term ”reverse” in RSA refers to the fact that artificial components are placed in reverse positions in the shoulder joint, compared to traditional replacements. While there aren’t specific subtypes of RSA, there are varieties of shoulder replacements that differ in design and technique. These can broadly be categorized into:
-
- Standard (anatomic) total shoulder replacement
-
- Partial (hemiarthroplasty) shoulder replacement
-
- Reverse total shoulder replacement (RSA)
Causes
The need for a reverse shoulder arthroplasty usually arises from chronic shoulder conditions or injuries, such as:
-
- Rotator cuff tear arthropathy: a combination of severe shoulder arthritis and a large rotator cuff tear.
-
- Osteoarthritis: a type of degenerative arthritis that occurs due to wear and tear of the joint.
-
- Rheumatoid arthritis: a chronic inflammatory disorder that can lead to joint deformity and erosion.
-
- Proximal humeral fractures: injury to the uppermost part of the arm bone, adjacent to the shoulder.
Symptoms
Patients considering RSA typically experience the following symptoms:
-
- Persistent, severe shoulder pain
-
- Inability to raise the arm above the head
-
- Restricted motion or weakness in the shoulder
-
- Inability to perform daily activities due to shoulder pain or mobility issues
Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination of the shoulder is typically the starting point for diagnosing shoulder pain. The strength, flexibility, and range of motion are assessed. Diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, can provide further detail, allowing physicians to see the structure of the shoulder, identify any damage, and determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment Options
Before resorting to RSA, most physicians will recommend non-surgical treatments to relieve pain and improve function. These may include physical therapy, pain medications, injections, or wearing a shoulder brace. However, if these treatments do not alleviate the symptoms, or if the shoulder condition becomes more severe, RSA may be suggested.
The goal of a reverse shoulder arthroplasty is to help you get back to doing the things you enjoy without pain and with improved function. During the procedure, the damaged parts of the shoulder are replaced with artificial components.
Living With Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Life after reverse shoulder arthroplasty involves a certain degree of recovery and rehabilitation. Here are some tips:
-
- Follow your doctor’s and physical therapist’s instructions about care and activity restrictions post-surgery.
-
- Perform a gradual return to normal activities, starting with gentle range-of-motion exercises.
-
- Beware of certain activities and movements that could lead to reinjury, such as heavy lifting or sudden twisting movements.
-
- Consistently attend physical therapy sessions and diligently complete at-home exercises to restore function and mobility.
In most cases, pain is significantly decreased and function is improved after surgery, allowing patients to return to many of their daily activities with greater comfort and ease.
When to Seek Help
While complications after RSA are uncommon, it’s important to consult your doctor immediately if you experience:
-
- Signs of infection like redness, warmth, increased swelling, or drainage at the surgical site.
-
- Increase in pain which is not relieved by medication.
-
- Change in sensation or color in the arm or hand, such as tingling, numbness, or paleness.
-
- Shortness of breath or chest pain.
Always remember that you are in good hands. Your healthcare team is there to help you through your journey, providing you with the necessary support, and answers to your questions and concerns.
