Rheumatoid Arthritis
Overview
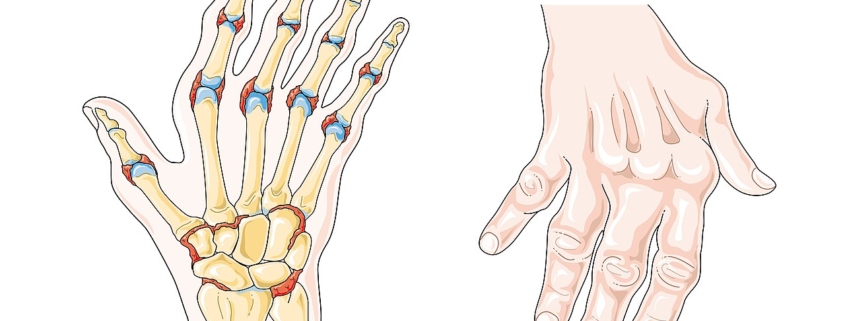
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, inflammatory disorder affecting more than 1.3 million people in the United States alone. It primarily affects the joints, causing swelling, stiffness and pain. Over time, this condition can lead to joint damage or deformity. Understanding this condition can help patients manage its symptoms effectively.
Types
Rheumatoid arthritis typically falls under two categories:
-
- Seropositive RA: This is the most common type of RA, characterized by the presence of anti-CCP (Antibodies to citrullinated protein) antibodies in the blood.
-
- Seronegative RA: In this type, these antibodies are missing, making the diagnosis more difficult.
Causes
While the exact cause of RA is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes may make you more susceptible to triggers like infection or trauma that can activate the disorder’s immune response.
Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms may vary in severity and may include:
-
- Joint pain and swelling
-
- Joint stiffness, particularly in the morning
-
- Fatigue, fever, and weight loss
Less common symptoms may include dry eyes and mouth, nodules under the skin, and inflammation in the lungs or heart.
Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, blood tests, and imaging, such as X-rays and ultrasound. The doctor will look for signs of inflammation as well as assess your joint function.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for RA, but treatments aim to control symptoms and prevent joint damage. Options include:
-
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
-
- Physical therapy: Can help to maintain mobility and strength.
-
- Surgery: If conservative treatments fail, surgery including joint fusion, synovectomy, or replacement may be considered.
Living With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Here are some practical ways to cope with RA:
-
- Regular Exercise: It can help maintain joint flexibility. Low-impact activities like swimming or walking are most beneficial.
-
- Balanced Diet: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage symptoms.
-
- Mental Health: It’s crucial to address mental health. Seek help if you’re feeling depressed or overwhelmed. Coping strategies like relaxation techniques, stress management, and connecting with a support group can offer immense help.
When to Seek Help
RA can worsen over time, causing severe damage if not managed well. If you’re experiencing unexplained joint pain and swelling that doesn’t resolve with rest, or if you’re diagnosed with RA and your symptoms worsen or don’t improve with treatment, seek immediate medical attention. Regular follow-ups with your doctor are crucial to managing this chronic condition effectively.
