Rotator Cuff Injuries
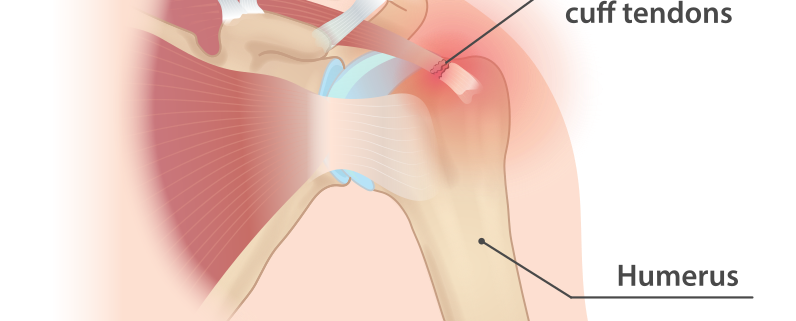
Overview
Rotator cuff injuries are a relatively common conditions that often affect those involved in heavy lifting or repetitive arm movements. Essentially, they refer to any injury to the group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, which are collectively known as the rotator cuff. These injuries can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility, but the good news is that there is a range of effective treatment options available.
Types
Rotator cuff injuries can take several forms – either as a result of an acute injury or chronic wear and tear. Here are the three main types:
-
- Rotator Cuff Tendinitis: This is inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder joint. It is usually seen in athletes or individuals who frequently use their shoulder for their work.
-
- Rotator Cuff Tears: These can range from partial thickness (slight tears in the tendon) to complete thickness (the tendon has entirely torn away from the bone). The severity of a tear usually correlates with the extent of pain and the level of function in the injured arm.
-
- Impingement Syndrome: This occurs when the shoulder blade presses on the rotator cuff when lifting the arm, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility.
Causes
Rotator cuff injuries are often caused by repeated overuse of the shoulder, leading to wear and tear of the tendons. This is commonly seen in athletes who play sports such as baseball and tennis that involve repetitive swinging motion. Furthermore, ageing can lead to degeneration of the tendons in the rotator cuff, increasing the risk of injury. Other causes can include falls, lifting heavy objects or traumatic injuries such as dislocation of the shoulder joint.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of rotator cuff injuries include:
-
- Pain in the shoulder, especially when lifting the arm
-
- Weakness in the shoulder
-
- Reduced range of motion
-
- Difficulty performing activities that involve moving the shoulder.
Less common symptoms can include of severe pain and sudden weakness, which may indicate a complete tear in the rotator cuff.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a rotator cuff injury usually involves a clinical examination by a healthcare provider, during which they check your shoulder for tenderness, swelling, and strength. They may also ask about your symptoms and medical history. In some cases, imaging procedures such as X-rays, MRI scans, or an ultrasound may be used to provide a more detailed view of the shoulder joint.
Treatment Options
Ranging from conservative to surgical, there are several treatment methods for managing rotator cuff injuries. A few of them are:
-
- Conservative treatments: These may include rest, ice, physical therapy, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
-
- Surgical treatments: In more severe or chronic cases, surgery may be needed to repair the torn tendon. The type of surgery depends upon the size and location of the tear. Post-surgery, a rehabilitation program is usually needed to regain strength and function in the shoulder.
Living With Rotator Cuff Injuries
If you have a rotator cuff injury, managing its symptoms and preventing further harm to the shoulder joint can be achieved through several strategies:
-
- Regular physiotherapy and exercises to strengthen the shoulder and improve flexibility
-
- Resting the shoulder and avoiding lifting heavy objects
-
- Regularly applying ice to the shoulder
-
- Taking over-the-counter pain relief as advised by a doctor
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical attention if you have sudden onset of severe pain, a snapping sensation, and an immediate weakness in your arm which may indicate that you’ve completely torn your rotator cuff. If you are experiencing chronic shoulder and arm pain or if the condition is interfering with your ability to perform everyday activities, consult with a healthcare provider.
Remember, early recognition and treatment can help prevent further injury and chronic shoulder problems. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice for optimal recovery from a rotator cuff injury.
