Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy
Overview:
Rotator cuff tear arthropathy refers to a unique and complex form of shoulder arthritis that can cause debilitating pain and impaired shoulder function. This condition primarily arises from a severe, long-term tear in the rotator cuff – a group of muscles and tendons encircling the shoulder joint. Its prevalence is most common in the elderly population, particularly individuals above the age of 70.
Types:
Rotator cuff tear arthropathy is specifically categorized under the umbrella term ‘shoulder arthropathy’, which includes several types of shoulder-related arthritis. Although not further classified into different types or subtypes, the severity of the condition can range from mild to severe, and can occur in either one or both shoulders.
Causes:
The chief cause of rotator cuff tear arthropathy is a chronic, unattended tear in the rotator cuff. When these tears remain unhealed, it leads to significant wear and tear of the shoulder joint over time. Other risk factors include:
– Aging: The risk of developing this condition increases with age.
– Rheumatoid arthritis: Patients with this autoimmune disorder are at higher risk.
– Genetic factors: Some studies suggest an inherited predisposition.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of rotator cuff tear arthropathy can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
– Severe shoulder pain, often worsening with movement.
– Gradual loss of shoulder movement and strength.
– Increased shoulder stiffness.
– Crackling sensation when moving the shoulder (crepitus).
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing rotator cuff tear arthropathy typically involves a combination of various tests and procedures:
– Physical examination: The doctor will assess your shoulder strength and range of motion.
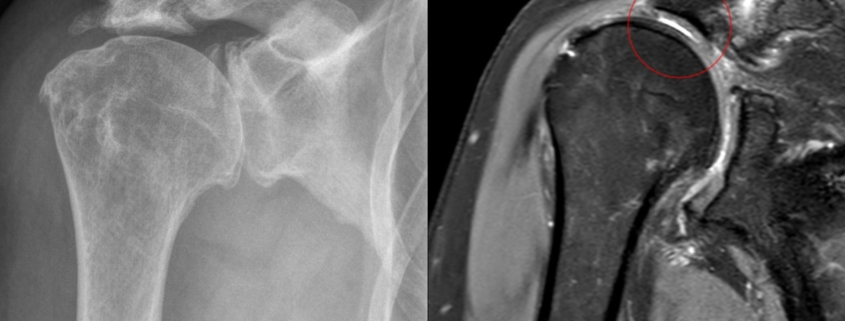
– Imaging tests: X-rays and MRIs can provide detailed images of your shoulder, allowing doctors to examine the rotator cuff muscles and joint surfaces in detail.
Treatment Options:
Both conservative and surgical treatment options are available for rotator cuff tear arthropathy. These can include:
– Physical therapy: Regular exercise under a physiotherapist’s guidance can strengthen your shoulder muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
– Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers or more potent prescribed medicines can help manage symptoms.
- Injections: Steroid injections might be used to reduce inflammation and offer temporary pain relief.
- Surgery: Severe cases may require shoulder joint replacement procedures.
Living With Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy:
Living with rotator cuff tear arthropathy can be challenging, but specific strategies can help manage the condition:
– Regular exercise: Maintain a routine of physician-approved exercises to keep your shoulder flexible and strong.
– Warm and cold treatments: Warm compresses or ice packs can help alleviate pain.
– Medication management: Take prescribed medications consistently and as directed by your doctor.
– Rest: Avoid overexerting your shoulder and allow it the necessary time to heal.
When to Seek Help:
If you experience severe shoulder pain, decreased mobility, or symptoms that persist despite conservative treatments, seek immediate medical attention. These could indicate advanced rotator cuff tear arthropathy or other severe shoulder conditions. Your health care provider can help determine the best course of action based on your symptoms and medical history. It’s vital to seek help early in order to prevent further damage and optimize treatment outcomes.
