Sacroiliac Joint Injections
Overview
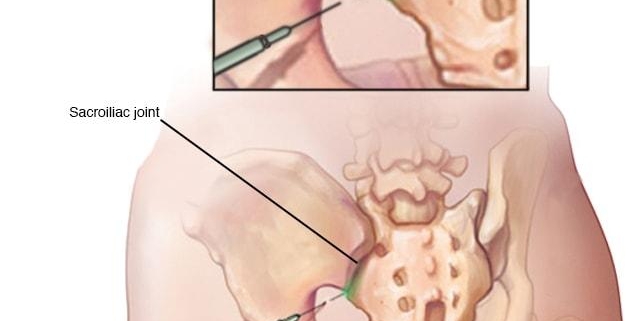
Sacroiliac joint injections, often shortened to SI joint injections, are minimally-invasive procedures used to diagnose and treat pain originating from your sacroiliac joint – the area where your lower spine and pelvis connect. According to research, about 15-30% of lower back pain cases are associated with the sacroiliac joint, making SI joint injections a common treatment for patients experiencing persistent discomfort in this area.
Types
There are two primary types of SI joint injections:
1. Diagnostic injections: The purpose of these injections is to confirm whether the sacroiliac joint is the source of pain. The injection contains a local pain-relieving anaesthetic.
2. Therapeutic injections: These are used to treat SI joint pain. They contain a corticosteroid, a powerful anti-inflammatory, to reduce swelling and pain.
It’s possible for a SI joint injection to serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes during the same procedure.
Causes
The causes of sacroiliac joint dysfunction, which lead to the need for SI joint injections, are diverse. They can result from:
- Direct injury to the area, such as a fall or car accident.
– Joint dysfunction: Either too much or too little movement can cause pain.
– Pregnancy: The ligaments around the joint naturally relax as the body prepares for childbirth, which can lead to increased stress on the sacroiliac joint.
– Overuse or strain from physical activities or specific occupations.
Symptoms
The primary symptom is lower back, hip or buttock pain, generally localized on one side. Other symptoms may include:
– Leg pain, usually in the back of the thigh.
– Difficulty standing up from a seated position.
– Increased pain when standing, climbing stairs or doing activities that put weight on the affected joint.
Diagnosis
Initial diagnosis involves a detailed review of your symptoms, medical history, and a physical examination including certain maneuvers to provoke SI joint pain. Additionally, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans or MRIs might be used. However, the most definitive way to diagnose sacroiliac joint dysfunction is through an SI joint injection, which can simultaneously diagnose and treat the condition.
Treatment Options
Apart from sacroiliac joint injections, other treatment options include:
– Conservative approaches: Physical therapy, use of painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, and heat or ice application.
- Hip joint injection or epidural steroid injections, depending on the pain source.
– In more severe cases, surgical intervention like sacroiliac joint fusion might be considered.
While every treatment approach has its merits, the choice depends on the severity of the symptoms, the patient’s overall health, and their personal preference.
Living With Sacroiliac Joint Injections
After the procedure, patients can expect some immediate relief due to the anaesthetic. However, a potential increase in pain might appear for 1-2 days after the procedure. Some tips to manage the condition post SI inject include:
– Avoid strenuous activities on the day of the injection.
– Apply ice to the site if you have any post-procedure discomfort.
– Resume normal activities the day after the procedure but listen to your body – don’t push it too hard.
– Remember, the steroids take a few days to work so you may not feel the full benefit of the injection immediately.
When to Seek Help
If your lower back, buttock or hip pain persists despite non-surgical treatments, or if it’s preventing you from performing normal activities, consider consulting with your doctor about SI joint injections. Additionally, if you experience severe post-injection symptoms such as fever, persistent pain, or redness/swelling at the injection site, seek immediate medical attention.
Understanding your body and knowing when and how to seek help are critical steps in managing and mitigating persistent pain. Remember, everyone’s journey is unique so it’s okay to ask questions, seek clarity, and express concerns about your condition or treatment.
