Septic Arthritis
Overview of Septic Arthritis
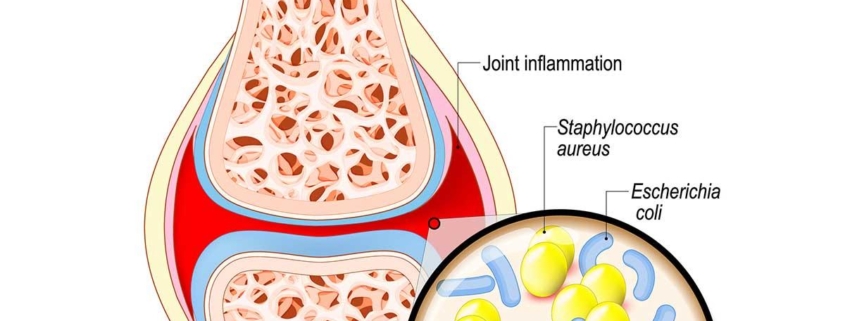
Septic Arthritis, also known as infectious arthritis, is a severe joint inflammation caused primarily by bacterial infection. Occasionally, viral or fungal infections can also play a role. Characterized by severe pain, swelling, and heat in the affected joint, it requires immediate medical attention due to its rapid and destructive nature, which can lead to lasting damage if untreated. Despite being a rare condition, its high risk ratio makes understanding this disease critical.
Types of Septic Arthritis
The two main types of septic arthritis are:
-
- Acute Septic Arthritis: It sets in quickly with intense symptoms. It’s most often caused by bacterial infection.
-
- Chronic Septic Arthritis: It develops slowly and is less intense initially. It’s usually the result of fungal or mycobacterial infections.
Causes of Septic Arthritis
Septic arthritis is often caused by bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus aureus or Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It usually occurs when bacteria, or other infectious agents, are carried through the bloodstream from another area of the body, such as the lungs or urinary tract, and deposited into a joint. However, it can also occur due to a direct injury or surgical procedure.
Risk factors include existing joint problems, a weakened immune system, certain medications, skin conditions and even drug misuse.
Symptoms of Septic Arthritis
The common symptoms of septic arthritis include:
-
- Severe joint pain that might worsen with movement
-
- Swelling and redness of the affected joint
-
- Fever
-
- Chills
-
- General weakness or fatigue
Less common symptoms could include loss of appetite and weight loss. While any joint can be affected, it most commonly involves the knees.
Diagnosis of Septic Arthritis
Diagnosis of septic arthritis typically involves laboratory analysis of joint fluid which is extracted with a needle. Blood tests may also be required to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection. Other imaging tests, like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may be used to identify joint damage.
Treatment Options
Treatment for septic arthritis aims to eliminate the infection with antibiotics and drain the infected joint fluid.
-
- Antibiotics: These are typically given intravenously in the hospital.
-
- Drainage: Infected joint fluid is usually removed, using needle aspiration or during surgery. The drainage may need to be repeated.
-
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to treat any damage to the joint or to better drain the infection.
Living With Septic Arthritis
Living with septic arthritis presents challenges, but with proper management, individuals can lead a normal life. It includes taking prescribed medications as directed by your doctor, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and regular exercise, and routine medical check-ups. It’s also beneficial to keep the spirit and stress levels in check.
When to Seek Help
If you’re experiencing severe joint pain, especially with fever, redness, and swelling, seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms can quickly escalate, and delaying treatment can lead to permanent joint damage or life-threatening complications from the spread of infection.
It’s worth repeating, septic arthritis is a medical emergency. Thus, timely recognition, diagnosis and treatment are crucial to a full recovery.
