Shoulder Arthritis
Overview
Shoulder arthritis is a health condition marked by inflammation, swelling, and pain in the shoulder joint. This medical issue is common, affecting millions around the world. It can significantly impair quality of life, limiting your daily activities. Understanding your condition is the first step towards managing it and reclaiming an active life.
Types
Shoulder arthritis is broadly categorized into three types:
1. Osteoarthritis (OA): Also known as wear-and-tear arthritis, it happens when the cartilage cushioning the ends of the bones wears downs over time.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease causing inflammation of the joint lining, causing pain and stiffness.
3. Posttraumatic Arthritis: Arthritis developing after an injury to the shoulder like a fracture or dislocation.
Causes
While the exact causes of shoulder arthritis may vary based on the type, some common risk factors include:
1. Increasing age: It’s more common in older adults.
2. Family history: Genetics plays a role.
3. Overuse of the shoulder: Regular, heavy lifting or intense physical activity can contribute to wear and tear.
4. Injuries or infections: These can increase your risk, especially if they’ve occurred in the past.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
1. Persistent pain in shoulders
2. Stiffness or reduced mobility
3. Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder area
4. A grinding or clicking sound during movement
Diagnosis
If shoulder arthritis is suspected, your doctor will typically begin with a medical history and physical examination. Further diagnostic steps may include:
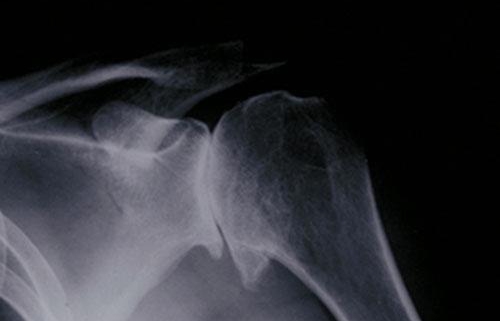
1. X-rays: Can reveal bone spurs, narrowing of the joint space, or other changes.
2. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This can provide a detailed image of the soft tissues, helping to detect more nuanced changes.
Treatment Options
While arthritis currently has no cure, various treatment options can manage symptoms and slow the disease’s progression:
1. Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used. In more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications.
2. Physical Therapy: Regular exercises will maintain joint flexibility and strengthen supporting muscles.
3. Surgery: If conservative treatments are ineffective, surgical procedures like joint replacement or arthroscopy can be considered.
Living With Shoulder Arthritis
Managing shoulder arthritis involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adaptations:
1. Regular Exercise: Maintain an active lifestyle but avoid tasks that put excessive strain on your shoulder.
2. Rest: Balance activity with rest to prevent overtaxing your shoulder.
3. Heat or Cold Therapy: Using warm compresses or cold packs can offer some temporary relief.
4. Medication Management: Take your prescribed medications consistently and report any side-effects to your doctor.
When to Seek Help
Seek immediate medical attention if your symptoms significantly worsen, you’re experiencing severe pain, your mobility becomes severely restricted, or you develop a fever or unexplained weight loss. These could signal a serious progression of your condition or a different medical problem requiring attention.
living with shoulder arthritis can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and care, most people with arthritis lead active and fulfilling lives. If you suspect you have shoulder arthritis, seek medical advice promptly for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
