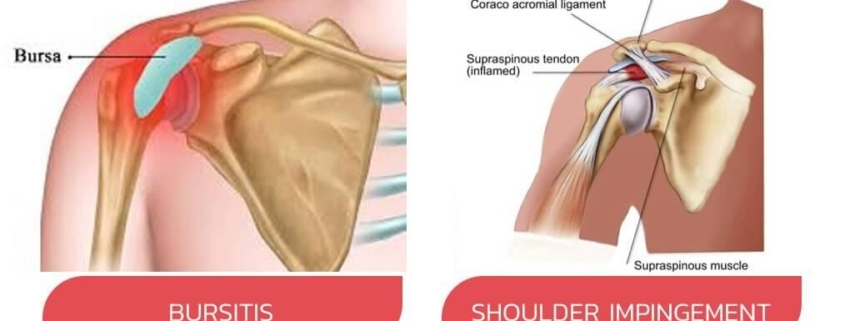
Shoulder Bursitis
Overview
Shoulder bursitis is a painful condition that affects the bursa, a small, fluid-filled sac located in your shoulder joint. It serves as a cushion between your bones and the surrounding soft tissues, helping your shoulder move without friction. Shoulder bursitis occurs when these bursae become inflamed, causing discomfort and limited motion. This condition affects a significant number of people, and anyone, regardless of age, can fall victim, though it’s more common in adults over the age of 50.
Types
While shoulder bursitis broadly involves inflammation of shoulder bursae, the condition can further be categorized into subtypes mainly based on the affected bursa. The most common type is subacromial bursitis, which affects the bursa located between the rotator cuff and the shoulder bone (acromion).
Causes
Shoulder bursitis is typically caused by:
-
- Repetitive, overhead movements of your arm
-
- Acute injuries or direct trauma to your shoulder
-
- Structural abnormalities or degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis
-
- Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis
Symptoms
Common symptoms of shoulder bursitis include:
-
- Pain and stiffness in your shoulder
-
- Sensitivity or tenderness around the joint
-
- Difficulty with overhead activities or sleeping on the affected side
-
- Loss of range of motion in your shoulder
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of shoulder bursitis typically involves a physical examination and a review of your medical history. Your doctor may ask about your symptoms, recent activities, and any past shoulder injuries. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound may also be used to get a detailed look at your shoulder and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for shoulder bursitis aims to reduce inflammation and pain, as well as restore function and prevent recurrence. Below are standard options:
-
- Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
-
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists can teach you exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion.
-
- Steroid Injections: If symptoms are severe, your doctor may suggest steroid injections for quick relief.
-
- Surgery: In rare cases, if symptoms do not improve with conservative methods, surgery may be necessary to remove the inflamed bursa.
Living With Shoulder Bursitis
Living with this condition involves managing pain and preventing recurrence. Keep in mind the following tips:
-
- Regular exercise: Strengthening your shoulder muscles can help protect the joints and reduce further injury risks.
-
- Heat and cold therapy: Applying ice packs can help control inflammation, while heat therapy can help ease stiffness.
-
- Pain management: Regular use of prescribed medications can control pain and inflammation.
-
- Mindful activity: Avoid repetitive overhead activities and take regular breaks when performing activities that involve shoulder use.
When to Seek Help
While shoulder bursitis can often be managed at home, you should seek immediate medical attention if:
-
- Your condition does not improve within two weeks of treatment
-
- The pain is affecting your ability to complete daily tasks
-
- You have fever, redness, swelling, or warmth around the shoulder, which might indicate an infection
