Spondyloarthropathies
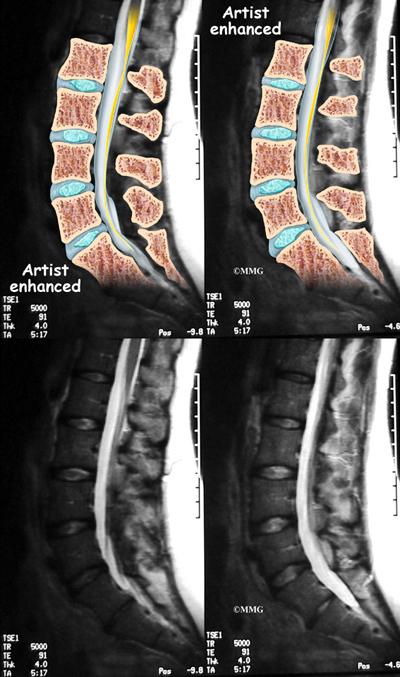
Overview of Spondyloarthropathies
Spondyloarthropathies are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases that primarily affect the spine and other joints. They’re a cause of long-term pain and physical disability, impacting the lives of millions worldwide. Studies estimate that nearly 1.7% of the adult population in the United States suffers from these conditions. Let’s unwrap this complicated medical term: “spondy” means spine, “arthro” refers to joint, and “pathy” stands for disorder. In essence, if you have a spondyloarthropathy, you have a joint disorder involving the spine.
Types of Spondyloarthropathies
Spondyloarthropathies consist of several related conditions:
-
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: This is the most common type, often causing inflammation in the spinal joints resulting in chronic pain and discomfort.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: This typically occurs in persons with psoriasis, a skin condition. The inflammation may not be limited to the spine and can affect other joints too.
- Reactive Arthritis: This form is often triggered by an infection in the body, such as intestinal or urinary tract infections. It typically lasts three to 12 months.
- Enteropathic Arthritis: This occurs in individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis.
Causes of Spondyloarthropathies
The exact cause of spondyloarthropathies is unknown. However, there are several risk factors believed to play a pivotal role, including:
-
- Genetics: Certain genes, such as HLA-B27, are associated with a higher risk of developing spondyloarthropathies.
- Age: Although these conditions can occur at any age, most people are diagnosed before the age of 45.
- Sex: Men are generally more at risk than women, particularly when it comes to Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Health History: Certain health conditions, like Psoriasis or certain gastrointestinal diseases, can predispose individuals to developing spondyloarthropathies.
Symptoms of Spondyloarthropathies
While symptoms can vary greatly depending on the specific type of spondyloarthropathy, common signs are:
-
- Persistent lower back pain and stiffness
-
- Joint pain and swelling
-
- Fatigue
-
- Neck pain
Less common symptoms can include:
-
- Skin problems, such as rashes or psoriasis
-
- Inflammation in the eyes
-
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
Diagnosis of Spondyloarthropathies
Diagnosis is based on a combination of a patient’s symptoms, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI.
Typically, doctors will first evaluate your symptoms and medical history. Blood tests can check for inflammation and the presence of HLA-B27, a genetic marker. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs can help visualize the affected joint and check for signs of inflammation and damage.
Treatment Options for Spondyloarthropathies
While there’s currently no cure for spondyloarthropathies, the goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms, slow the disease’s progression, and maintain a good quality of life. The treatment may include:
-
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications
-
- Immunosuppressants or biologics to reduce the immune system’s overactivity
-
- Physical therapy to maintain posture and flexibility
-
- In severe cases, joint replacement or spinal surgery may be necessary
Living With Spondyloarthropathies
Having a chronic disease can be challenging, but there are several strategies to enhance quality of life:
-
- Exercise Regularly: Keeping your body active can relieve stiffness and maintain joint flexibility.
- Stay Informed: Learning about your condition can help you manage it better and communicate effectively with your healthcare team.
- Eat Healthy: A balanced diet can aid in reducing inflammation.
- Rest and Relaxation: Don’t overlook the importance of getting enough sleep and managing stress levels.
When to Seek Help for Spondyloarthropathies
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider is essential. But seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe symptoms such as:
-
- Extreme fatigue
-
- Sudden vision changes or eye pain
-
- Unexplained weight loss
-
- Fever, chills, or uncontrolled diarrhea
These conditions can be challenging, but with appropriate management and care, most individuals can maintain active, fulfilling lives despite their diagnoses. This guide is meant to provide general knowledge. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personal medical advice.
