Sternoclavicular Joint Problems
Overview
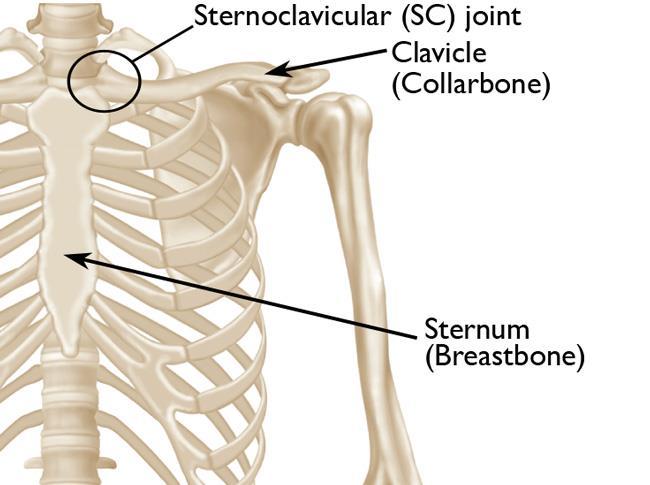
The sternoclavicular (SC) joint is a small joint located at the base of the neck, where the clavicle (collarbone) meets the sternum (breastbone). Despite being a small joint, it plays a crucial role in the movement of the upper body, especially the shoulders and arms. Sternoclavicular joint problems, although not very common, can cause discomfort and limit movement.
Types
Sternoclavicular joint problems can generally fall into four categories:
-
- Arthritis: This is when the joint becomes inflamed due to cartilage wearing down over time. It is often a result of aging but can also be due to traumatic injuries.
-
- Infection: Infections in the SC joint are rare but can occur due to medical procedures, injuries, or conditions that weaken the immune system.
-
- Dislocation: This happens when the joint is forcibly moved or shifted out of its usual position, typically due to a traumatic event.
-
- Tumor: Although quite rare, tumors can originate in or spread to the SC joint causing pain and inflammation.
Causes
SC joint problems can be caused by various factors including:
-
- Physical trauma or injury to the chest or shoulder
-
- Arthritic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis
-
- Bacterial or fungal infections
-
- Certain activities or sports that put repeated stress on the chest or shoulder area
-
- Abnormalities in the joint that are present at birth
Symptoms
Common symptoms of SC joint problems can include:
-
- Pain or discomfort in the joint, especially when moving the shoulder or arm
-
- Swelling or inflammation of the joint
-
- Tenderness and warmth over the joint
-
- Visible deformity due to dislocation or other issues
-
- Reduced ability to move the affected side
Diagnosis
Diagnosing SC joint problems usually involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging tests. Your healthcare provider may start with a detailed medical history and a physical exam to check for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion of the joint. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be used to get a clearer picture of the joint and any potential problems.
Treatment Options
Treating SC joint problems often begins with conservative methods such as:
-
- Rest and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms
-
- Ice and heat therapy to relieve inflammation and pain
-
- Over-the-counter pain medications and anti-inflammatories
-
- Physical therapy exercises to strengthen muscles around the joint and improve its mobility
-
- Wearing a shoulder brace to provide support
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical options such as joint resection, ligament reconstruction, or joint replacement may be considered, depending on the severity of the condition.
Living With Sternoclavicular Joint Problems
Living with SC joint problems can present certain challenges, but with the right management strategies, most individuals can lead an active and fulfilling life. Here are some tips:
-
- Stay active with low-impact activities such as swimming or yoga that allows gentle movement of the joint without straining it.
-
- Manage your pain, whether with over-the-counter medications or prescription drugs, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
-
- Follow a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods to help manage symptoms.
-
- Get plenty of rest to give your body time to heal.
-
- Regularly perform the exercises recommended by your physical therapist to keep the joint flexible and strong.
When to Seek Help
While some discomfort with SC joint problems can be managed at home, you should seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
-
- Intense pain
-
- Redness, heat, or swelling over the joint
-
- Sudden decrease in the ability to move your shoulder or arm
-
- Any signs of infection such as a fever or chills
Always consult your healthcare provider further if you’re experiencing ongoing discomfort or if your symptoms worsen. Each individual is unique, and your treatment plan should be tailored to your specific needs for the best outcome.
