Thoracic Disc Herniation
Overview
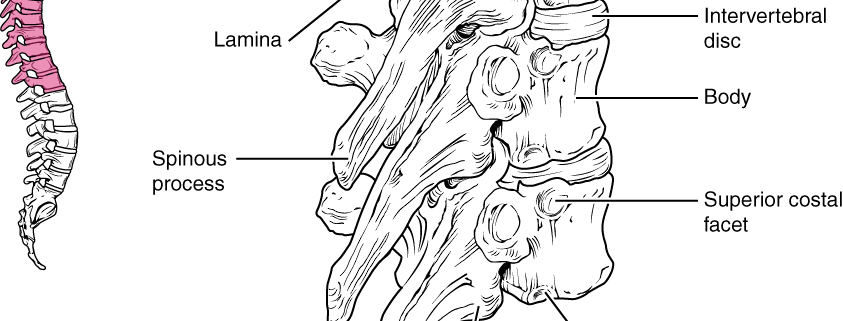
A thoracic disc herniation refers to a health issue occurring when one of the intervertebral discs in the upper back or middle back, also known as the thoracic spine, bulges or ruptures out of place. It’s a relatively rare condition, accounting for only about 1% of all disc herniations.
The human spine is made up of small bones known as vertebrae stacked on top of each other. In between these bones are discs, which act as shock absorbers, allowing flexibility and preventing the vertebrae from grinding against each other. When one of these discs sustains damage, it can herniate, which means the disc’s inner material is forced out, putting pressure on the nearby spinal cord or nerve roots.
Types
As thoracic disc herniation is relatively rare, they are often classified according to the direction of the disc herniation. They can generally be of three types:
1. Central Thoracic Disc Herniation: The disc bulges directly into the spinal canal
2. Lateral Thoracic Disc Herniation: The disc bulges sideways, into the nerve root
3. Sequestrated Thoracic Disc Herniation: This happens when the disc material breaks off into the spinal canal
Causes
Thoracic disc herniation can result from a variety of causes, including:
– Aging: As part of the natural aging process, these discs can lose their elasticity, height, and water content, making them more vulnerable to damage.
– Trauma: Accidents or injuries leading to forceful impacts can cause discs to herniate.
– Spinal Conditions: Diseases such as Degenerative Disc Disease can increase the risk of developing a thoracic disc herniation.
Symptoms
The myriad symptoms of thoracic disc herniation can vary depending on the location and severity of the problem. Key symptoms include:
– Mid to upper back pain
– Radiating pain around the chest or abdomen
– Weakness in the legs
– Changes in bowel or bladder function
In some instances, you may have a herniated thoracic disc and not even know it as it produces no symptoms.
Diagnosis
A thoracic disc herniation diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
– Physical examination: Your doctor will assess your symptoms and perform a physical evaluation.
– Imaging tests: These might include X-rays, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computerized Tomography (CT) scans. These images allow the doctor to visualize the herniated disc in detail.
- Myelogram: A dye is injected into the spinal fluid, and then an X-ray is taken. This provides a clear image of the nerve roots and spinal cord.
Treatment Options
There are various thoracic disc herniation treatment options. Non-surgical treatments are usually tried first, which may involve:
– Physical therapy: Strengthening the muscles supporting the thoracic spine can reduce pressure on the herniated disc.
– Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and nerve pain medications can help manage the pain.
If these methods do not alleviate symptoms, or if the herniation is severe, surgery may be considered.
Living With Thoracic Disc Herniation
Living with a thoracic disc herniation can impact the life of the affected individual daily. However, certain steps can help in managing the condition:
– Regular Exercise: Maintain a regular exercise routine that focuses on stretching and strengthening the back and core muscles.
– Good Posture: Maintain good posture while working, sitting, and sleeping to alleviate pressure off the affected discs.
– Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the load on your vertebrae and discs.
– Medication Management: Take prescribed medications consistently as directed by your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Help
Immediate medical attention is required if your symptoms worsen, or if you experience severe pain, weakness in your muscles, or changes in bowel or bladder function. These could be signs of a serious condition called cauda equina syndrome, a rare but severe compression of the nerves at the end of the spinal cord.
Remember, while thoracic disc herniation may be a rare condition, it’s crucial to seek medical advice and proper treatment when necessary. With proper management strategies, you can reduce discomfort and enhance your quality of life.
