Tibial Osteotomy
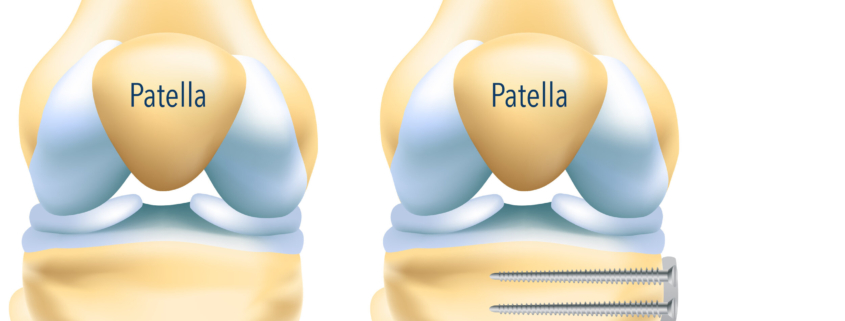
Overview
Tibial osteotomy is a surgical procedure to rectify misalignment and biomechanical imbalances in the knee. It is a form of treatment to manage osteoarthritis, a common knee condition prevalent in older adults. This treatment corrects the body’s weight distribution by shifting the load to healthier, less worn-out parts of the knee, thus reducing pain and improving joint function.
Types
There are two major types of tibial osteotomy:
-
- High tibial osteotomy (HTO): This procedure is often utilized when only the inner part of the knee joint is worn out or damaged.
- Distal tibial osteotomy (DTO): Common for individuals experiencing instability or malalignment in the ankle joint. The lower part of the shinbone (distal tibia) is realigned in this type of procedure.
Causes
Osteoarthritis is the leading cause for a tibial osteotomy procedure. Other causes are knee injuries and joint conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Risk factors include age, obesity, genetics, previous injury, and strenuous physical activities.
Symptoms
Common symptoms warranting a tibial osteotomy include:
-
- Constant knee pain or discomfort
-
- Limited range of motion in the knee
-
- Noticeable knee deformities
-
- Difficulty walking or performing daily activities
Diagnosis
A tibial osteotomy is often considered after a thorough assessment by your doctor, which includes a detailed case history, physical examination, X-Rays, and other imaging tests if necessary.
Treatment Options
Before opting for surgery, doctors often suggest non-invasive treatments like physiotherapy, weight management, and pain management medications. If these conservative methods don’t reduce the symptoms, a tibial osteotomy may be recommended.
Living With Tibial Osteotomy
Recovery from a tibial osteotomy takes time and requires patience. Some key points to managing post-surgery include:
-
- Physical Therapy: Regular and guided exercises help regain strength and movement.
-
- Pain and swelling management: Using ice compresses and prescribed pain medication.
-
- Weight management: Keeping a healthy weight helps reduce stress on the knee.
-
- Regular doctor check-ups: Ensuring your recovery is on track.
When to Seek Help
After a tibial osteotomy, seek immediate medical attention if you notice:
-
- Signs of infection like increased swelling, redness, or persistent pain
-
- Breathlessness or chest pain, which could indicate a blood clot
-
- Any drainage from the surgery site
Taking care of your health after a tibial osteotomy is crucial for a successful recovery. With care, guidance, and a good rehabilitation plan, a person can return to their regular activities, significantly enhancing their quality of life.
