Transient Synovitis
Overview: What is Transient Synovitis?
Transient Synovitis, also known as toxic synovitis, is an inflammation of the hip joint that is characterized by sudden onset hip pain. It is the single most common cause of acute hip pain in children, though adults can also be affected. Typically, it is a temporary condition that resolves on its own over time without causing lasting damage to the hip.
Types: Are there different kinds of Transient Synovitis?
As transient synovitis is a specific type of inflammatory condition affecting the hip joint, there are no subtypes to further categorize the condition. The inflammation is similar across all cases, but the severity and duration of symptoms can vary among patients.
Causes: What leads to Transient Synovitis?
The exact cause of transient synovitis is currently unknown. However, it is widely believed to be triggered by a viral infection or an allergic reaction. In some cases, it may even follow a minor trauma to the hip. Certain populations, like children between the ages of 3 to 10 and males, are more susceptible to developing this condition.
Symptoms: How does Transient Synovitis manifest itself?
Transient synovitis primarily presents with hip pain, which can lead to a limp or difficulty walking. Other common symptoms include:
-
- Thigh or knee pain
-
- Slight fever
-
- Reduced range of motion in the hip
In some cases, the patient might also experience abdominal pain or present viral symptoms like cough, runny nose, or sore throat.
Diagnosis: How is Transient Synovitis identified?
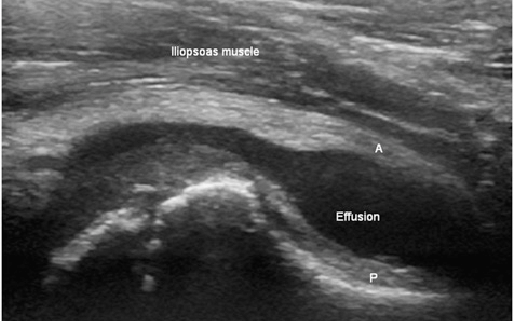
Diagnosis of transient synovitis involves a thorough physical examination followed by advanced imaging tests. Your doctor will often conduct blood tests to rule out other sources of hip pain like a bacterial infection. An ultrasound or an MRI can also be ordered to get a clear picture of the hip joint.
Treatment Options: How is Transient Synovitis managed?
The primary goal of treatment is to minimize pain and inflammation until the condition resolves on its own. Common treatment options include:
-
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
- Rest and avoidance of weight-bearing activities
-
- Physical therapy to improve joint mobility
In case of severe pain, a small amount of fluid may be withdrawn from the joint to reduce pressure.
Living With Transient Synovitis
Living with transient synovitis involves effective symptom management until the condition subsides. Here are some practical tips:
-
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with balanced diet and regular exercise to aid recovery
-
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers as directed by your healthcare provider
-
- Ensure regular, but gentle, movement of the affected joint to prevent stiffness
-
- Follow the prescribed physical therapy regimen diligently
-
- Regularly monitor temperature as even a slight fever may need medical attention
When to Seek Help
While transient synovitis usually resolves on its own, immediate medical attention should be sought if:
-
- The hip pain intensifies
-
- The patient is unable to move the affected leg or walk
-
- The hip joint looks swollen or red
-
- There is persistent fever
Remember, early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the discomfort associated with transient synovitis and speed up recovery.
