Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries
Overview
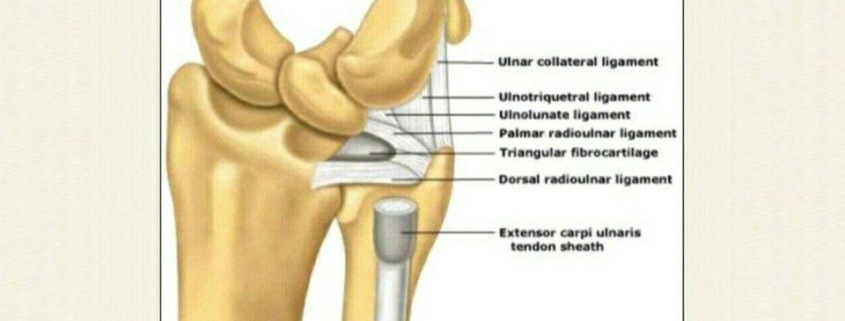
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) injuries relate to a condition affecting the wrist. The TFCC is a cluster of ligaments and cartilage tissues in the wrist that provides stability, cushioning, and smooth movements. When injured, this area can cause significant pain and disability. Many people may experience a TFCC injury, mainly athletes and people involved in repetitive manual tasks.
Types
TFCC injuries can generally be classified into two types:
1. Traumatic injuries: These are related to a sudden impact or injury, such as a fall on an outstretched hand.
2. Degenerative injuries: These are wear-and-tear injuries that happen gradually over time, usually associated with aging or repetitive movements.
Causes
TFCC injuries can be brought about by various factors. Trauma is a frequent cause, such as a fall onto an extended hand or a sudden twisting motion of the wrist. Repeated strain on the wrist, especially in sports such as tennis or golf, can also cause TFCC injuries. Age-related wear and tear is another factor, as the cartilage naturally weakens and becomes more vulnerable to damage over time.
Symptoms
Common symptoms associated with TFCC injuries include:
– Pain on the outside of the wrist
– Swelling in the wrist
- Difficulty moving or turning the wrist
– A feeling of clicking, crunching, or snapping in the wrist
– Weakness or instability in the wrist
Less common symptoms also include tingling or numbness, particularly in the pinky or ring fingers.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a TFCC injury typically starts with a thorough physical examination of the wrist. A healthcare provider may ask about the onset of symptoms, any related incidents (such as trauma), and the severity of pain or impairment.
Tests to confirm a diagnosis may include:
– X-rays to rule out bone fractures
– Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to visualize the soft tissues
– Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure employing a tiny camera to examine the inside of the wrist
Treatment Options
Treatment for TFCC injuries varies based on the severity of the injury and the patient’s daily needs:
1. Non-surgical treatment: This approach usually includes a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevated (RICE) treatment, alongside non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation. A splint or cast may be used to immobilize the wrist, allowing it to heal.
2. Physical Therapy: Once the initial inflammation and pain are managed, a physical therapist may recommend exercises to regain wrist strength and flexibility.
3. Surgical treatment: If conservative treatment methods don’t alleviate the symptoms, or in cases of severe injury, surgery may be necessary. Depending on the specifics of the injury, options may include arthroscopic surgery or open surgery.
Living With Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries
Living with a TFCC injury can be challenging, but several strategies can help manage the condition. Keep in mind the following:
- Consistently follow your treatment plan and attend all medical follow-up appointments.
– Avoid activities that exacerbate wrist pain.
– Practice daily wrist-strengthening exercises recommended by the physical therapist.
– Use over-the-counter pain relief medication as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Apply an ice pack to the injured area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
When to Seek Help
It’s crucial to seek medical help immediately if you experience a sudden onset of extreme wrist pain, especially following an accident or fall. Any noticeable deformity, intense swelling, and inability to move the wrist call for prompt medical attention.
In non-emergency situations, if you persistently have wrist pain, weakness, or a clicking or popping sensation, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment of TFCC injuries can significantly improve prognosis and ease the strain on daily life.
