Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip
Overview
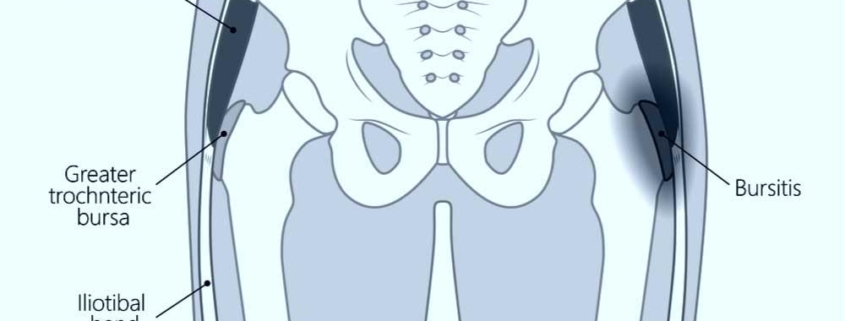
Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip is a common health condition that causes pain and discomfort in the outer part of the hip joint. This condition occurs when the bursa, a small, fluid-filled sac that serves as a cushion between bone and soft tissues, becomes inflamed. Nearly 1 in 4 individuals who are middle-aged or older experience trochanteric bursitis at some point. This condition can affect anyone, but it’s more commonly observed in middle-aged or older women.
Types
There aren’t specific types of Trochanteric Bursitis, however, it can either be septic or aseptic. Septic bursitis is rare and occurs when the bursa becomes infected. Aseptic bursitis, which is more common, refers to non-infectious inflammation of the bursa generally caused by injury or overuse.
Causes
Trochanteric Bursitis can be caused by various factors, which include:
-
- Repetitive stress or overuse: Regularly participating in activities that put pressure on the hip bursa, such as running or cycling, can lead to inflammation.
-
- Injury: A direct blow to the hip could lead to bursitis.
-
- Improper posture: Sitting or standing improperly for long periods can put excess pressure on the bursa.
-
- Medical conditions: Certain diseases, like arthritis or diabetes, could increase the risk of developing bursitis.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis include:
-
- Pain on the outer side of the hip.
-
- Increased pain when walking or during other physical activities.
-
- Pain that becomes worse at night, especially when sleeping on the affected hip.
-
- Swelling and tenderness on the hip.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Trochanteric Bursitis typically includes a physical examination where the doctor will apply pressure to the outer side of the hip to check for pain. The doctor may also examine the patient’s ability to move the hip joint. In some cases, imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that could cause similar symptoms.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Trochanteric Bursitis aims at reducing pain and inflammation. This typically involves:
-
- Rest: Limiting activities that worsen the symptoms can help in recovery.
-
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to relieve pain and reduce swelling.
-
- Physical therapy: Certain exercises can improve hip strength and flexibility, which can prevent future occurrences.
-
- Injections: If other treatments are ineffective, corticosteroid injections can be used to decrease inflammation.
-
- Surgery: In rare cases, if the condition doesn’t respond to other treatments, a surgical procedure to remove the bursa may be necessary.
Living With Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip
Living with trochanteric bursitis can be challenging, but with the right strategies and lifestyle changes, the condition can be managed effectively. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and using proper posture can help reduce the risk of bursitis. Over-the-counter pain medications can help manage discomfort, and heat or ice packs can provide relief. It’s also important to take rest periods during activities to avoid overexertion.
When to Seek Help
While Trochanteric Bursitis is typically manageable with conservative treatments, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if:
-
- The pain is severe or disabling.
-
- The pain doesn’t improve after two weeks of home treatment.
-
- The hip is red, swollen, or warm to the touch.
-
- You have a fever along with the hip pain.
Remember, early diagnosis and treatment can help speed up recovery and prevent the condition from worsening.
