Trochanteric Bursitis Surgery
Overview
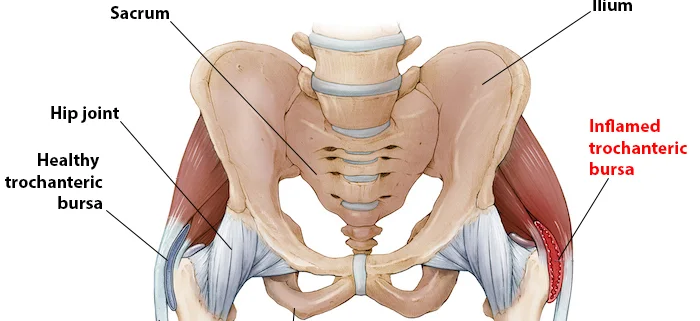
Trochanteric bursitis is a common orthopedic condition that often affects active individuals and the elderly. It occurs when the bursa, a fluid-filled sac near the hip joint, becomes inflamed, causing pain and discomfort. According to data, trochanteric bursitis accounts for approximately 20% of hip complaints in patients. Although painful, the good news is that appropriate treatment steps can effectively manage its symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
Types
Generally, there are two types of trochanteric bursitis:
-
- Acute Trochanteric Bursitis: This is a sudden inflammation of the bursa resulting from an injury or overuse.
-
- Chronic Trochanteric Bursitis: This type involves long-term inflammation and is often due to repetitive minor traumas or neglecting an acute condition.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of trochanteric bursitis:
-
- Injuries to the hip
-
- Overuse from repetitive activities such as running
-
- Poor posture
-
- Underlying conditions like arthritis or hip injuries
-
- Certain infections or diseases
Symptoms
The key symptom of trochanteric bursitis is pain on the outer part of the hip, which may extend to the thigh. This pain usually increases with movement and can be more severe during the night. Less common symptoms include:
-
- Swelling over the hip area
-
- Redness in the affected area
-
- Difficulty moving or walking
Diagnosis
A healthcare practitioner will diagnose trochanteric bursitis based on your medical history and a physical examination. They might ask about your symptoms and the types of activities you regularly engage in. Further tests such as X-rays, ultrasound or MRI may be used to distinguish it from other hip-related conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition. Options include:
-
- Conservative: Most cases respond well to non-invasive methods. Rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, physical therapy, and corticosteroid injections are common treatments.
-
- Surgical: In severe cases not responding to conservative measures, surgery may be considered. This involves removing the inflamed bursa through minimally invasive techniques.
Living With Trochanteric Bursitis Surgery
Post-surgery, recovery might involve some discomfort and limited mobility. You will likely need to follow a physical therapy program to improve flexibility and strength in your hip. Here are some general guidelines:
-
- Complete your physical therapy diligently.
-
- Limit activities that increase pain or swelling.
-
- Maintain a healthy weight to decrease stress on your hips.
-
- Consider gentle exercises like yoga or swimming.
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent or worsening hip pain, don’t hesitate to seek medical help. Specifically, you should consult your doctor if:
-
- Your pain does not improve with over-the-counter pain relievers.
-
- You have difficulty walking or doing daily activities because of your hip pain.
-
- You have a fever or the hip area looks red or swollen, which could be signs of an infection.
Although trochanteric bursitis can disrupt your life, understanding and managing the condition properly can lead to a swift recovery.
