Whiplash
Overview: Understanding Whiplash
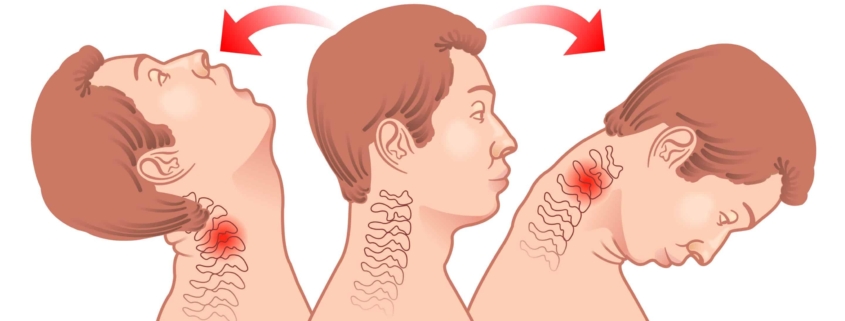
Whiplash is a common kind of neck injury triggered by a sudden rapid forward and backward movement of the neck, often associated with car accidents. Going beyond just car accidents, whiplash can result from sports injuries, physical abuse, and other types of traumas such as a fall. Whiplash can cause an array of symptoms, including neck pain, which sometimes surfaces only after a delay, thus eliciting the need for early diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Whiplash
There are primarily two types of whiplash injuries:
1. Acute Whiplash Injury: This occurs immediately after the incident and symptoms last for a shorter period (up to 6 months).
2. Chronic Whiplash: If symptoms persist for more than 6 months, the condition is classified as chronic whiplash.
Causes of Whiplash
Whiplash happens when your neck undergoes a forceful, rapid back-and-forth movement, much like the cracking of a whip, hence the name. Car accidents are the main cause, especially rear-end collisions. Other causes include physical abuses, like being punched, shaken, or during contact sports such as football.
Symptoms Associated with Whiplash
Symptoms of whiplash may appear right after the injury, or may take a few hours to several days to surface. These include:
– Neck pain and stiffness
– Worsening of pain with neck movement
– Loss of range of motion in the neck
- Headaches, usually starting at the base of the skull
– Fatigue or dizziness
– Less common signs are blurred vision, sleep disturbances, memory problems, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
Diagnosing Whiplash
A diagnosis of whiplash usually involves:
– Medical history: The doctor will ask for details about the accident or event that led to the injury.
– Physical examination: This may involve feeling for areas of tenderness, moving the head, arms, and shoulders in certain ways to check for pain and range of motion.
– Imaging tests: Depending on the severity, X-rays, CT scans, or MRI might be ordered to rule out any other neck or spinal damages.
Treatment Options for Whiplash
Treatment for whiplash is aimed at managing pain, restoring normal function in your neck, and getting back to your regular activities. This might involve:
– Over-the-counter pain medications
– Prescription medications
- Injections for muscle pain
- Exercises and physical therapy
Living With Whiplash
For many people, whiplash symptoms can resolve within a few weeks. While recovery, these strategies can help:
– Regularly practice neck exercises and stretches recommended by a physical therapist.
– Heat or cold can relieve the pain. Use heat pad or cold pack on your neck for 15 minutes every 2-3 hours.
– Over-the-counter pain relievers can assist with mild pain.
When to Seek Help
If you’ve been in a car accident or suffered another kind of trauma that hurt your neck, seek medical help. Do not neglect if the pain or symptoms persist even after a few weeks of self-care measures. Consult your doctor immediately if symptoms worsen, or if you have severe neck pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling in your arms or hands.
Remember, whiplash, if not treated promptly, can lead to chronic pain and long-term complications. Understanding the condition and taking prompt action can help to recover quickly and avoid further difficulties.
